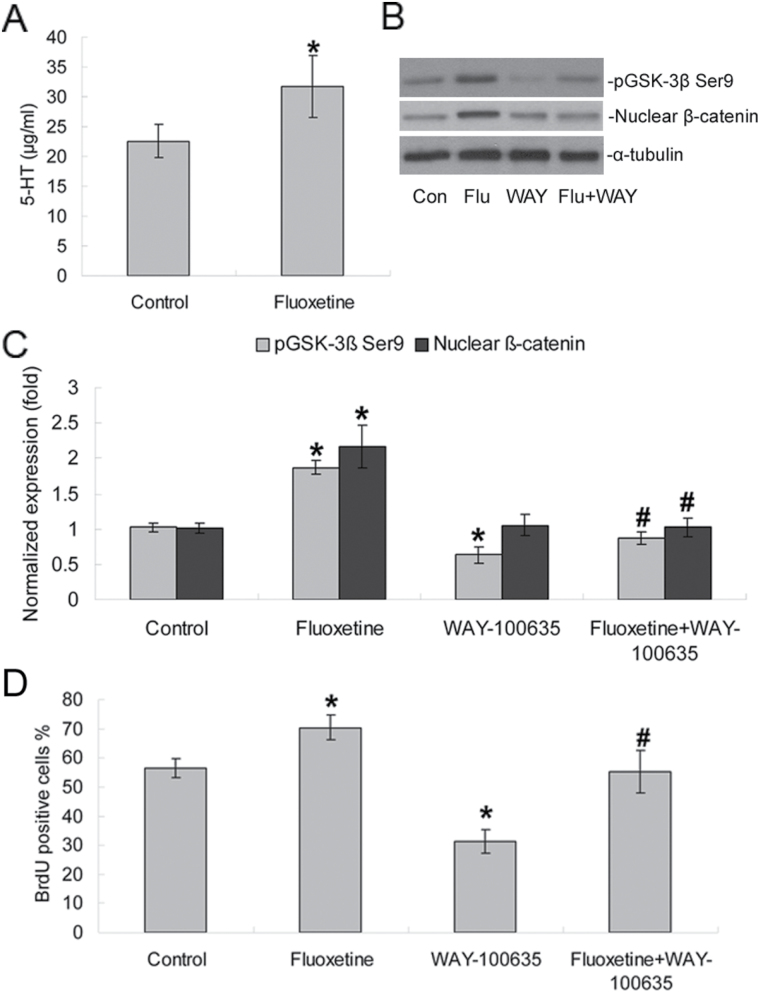
Figure 7.
Fluoxetine-induced enhancement of phosphorylation of Ser9 on GSK-3β and nuclear β-catenin depends on 5-HT1A receptors. (A) The ELISA showed that 1 μM fluoxetine increased 5-HT concentration in the culture media in NPC proliferation phases (n = 5 each). *p < 0.01 versus the control group. (B) Fluoxetine enhanced the phosphorylation of Ser9 on GSK-3β and nuclear β-catenin protein expression via 5-HT1A receptors. (C) Quantification of Western blotting signals of phospho-Ser9-GSK-3β, nuclear β-catenin, and α-tubulin proteins. Data were ratios compared with α-tubulin protein. Values represent means ± SD. n = 5 for each group. *p < 0.05 compared with the control group, #p < 0.05 versus the fluoxetine group. (D) WAY-100635 reversed fluoxetine-mediated proliferation of NPC. Analyses of variance revealed significant effects of fluoxetine and WAY-100635 on NPC proliferation [F (1, 18) = 72.20, p < 0.0001 for fluoxetine; F (1, 18) = 81.61, p < 0.0001 for WAY-100635]. Values represent means ± SD (n = 5). *p < 0.01 versus control; #p < 0.05 versus fluoxetine group. 5-HT1A, 5-hydroxytryptamine-1A; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta; NPCs, neural precursor cells; SD, standard deviation.