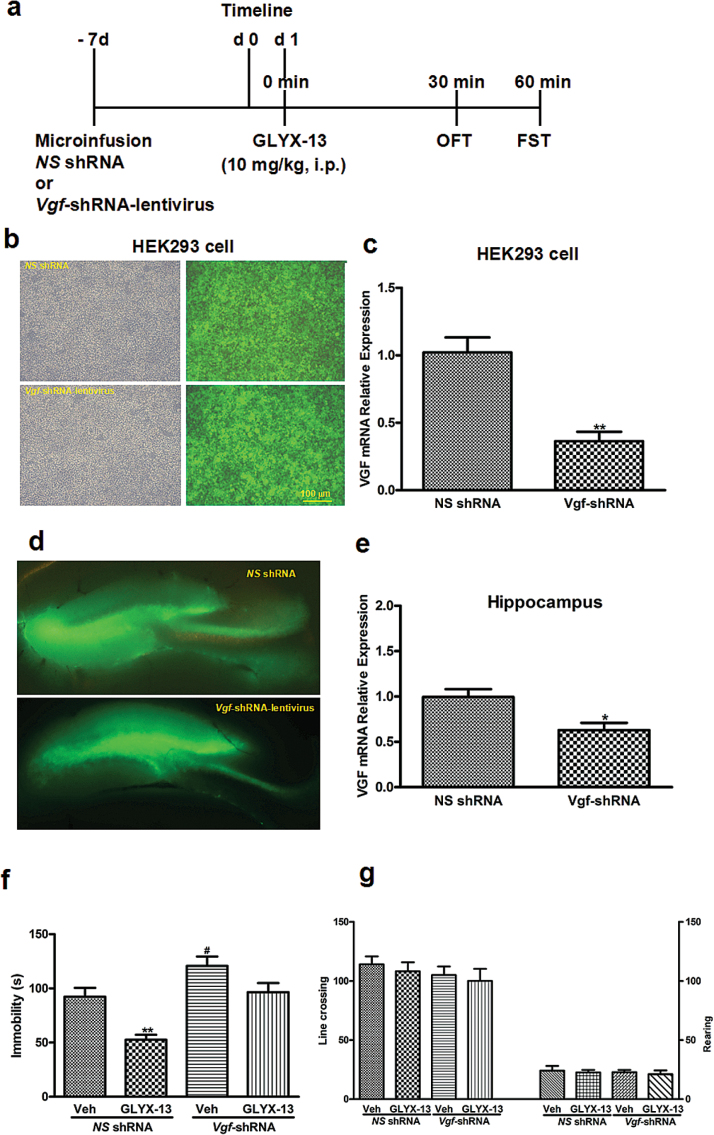
Figure 4.
Vgf knockdown in hippocampus blocks the rapid-acting antidepressant-like effects of GLYX-13. (a) Experimental procedure for the test schedule. NS shRNA or Vgf shRNA were microinfused into bilateral hippocampus of mice following 7-day acclimatization. GLYX-13 (10mg/kg, i.p.) or its vehicle was administrated beginning from 7 days after the viral infusions (day 1) and then 30 or 60 minutes later, the open field test (OFT) or forced swim test (FST) was conducted, respectively. (b) NS-shRNA or Vgf-shRNA were well expressed in HEK293 cells as indicated by EGFP (green) observed under a fluorescence microscope. Scale bar=100 μm. (c) The results are expressed as 2-△Ct [△Ct=Ct (VGF) – Ct (β-actin)] and normalized by the level of β-actin. (d) Microinjection sites and specific expressions of EGFP (green) in the hippocampus observed under fluorescence microscopy. Scale bars=200 μm. (e) The hippocampus tissues of 2mm in diameter around the injection site were punched out for qRT-PCR. (f) Vgf knockdown in the hippocampus significantly produced the depressive-like behavior and also blocked the antidepressant-like behavior in the FST of mice. (g) All the treatments had no effects on locomotor activity, reflected by the line crossings (left) and rearings (right) in mice. The data are expressed as mean±SEM (n=5 per group for VGF mRNA expression and n=9 per group for behavioral tests). **P<.01 (c), compared with NS shRNA group and **P<.01 (d), compared with Vehicle+NS shRNA group; #P<.05, compared with Vehicle+NS shRNA group.