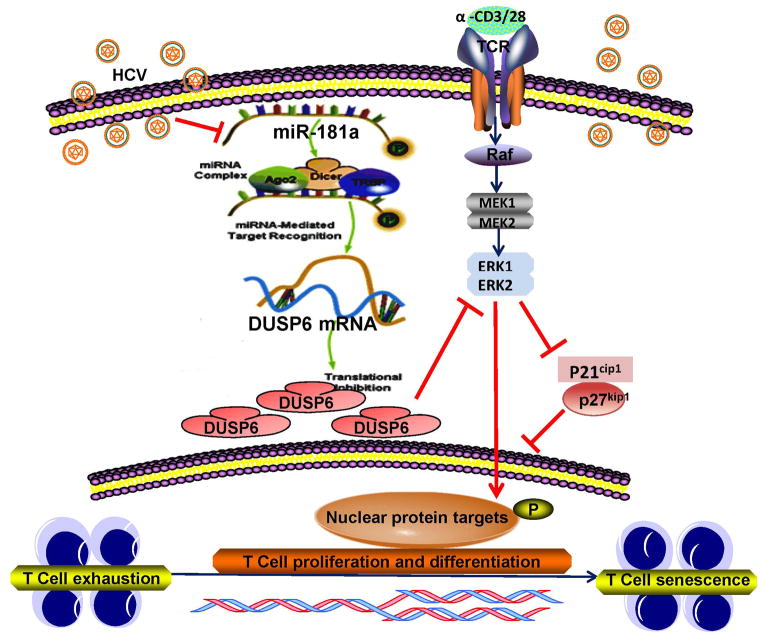
Fig. 6. Schematic model for premature T cell aging by HCV-induced, miR-181a-mediated DUSP6 regulatory signaling pathways.
HCV-induced decline of miR-181a expression facilitates DUSP6 over-expression in CD4+ T cells. This, in turn, may negatively affect the TCR-induced signaling pathways, such as ERK/MAPK phosphorylation and then alters cell cycle regulators p21cip1/p27kip1 and cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) activities. Therefore, reconstitution of miR-181a and/or inhibition of DUSP6 may provide a novel approach to improve T cell responses in virally infected individuals.