Figure 2.
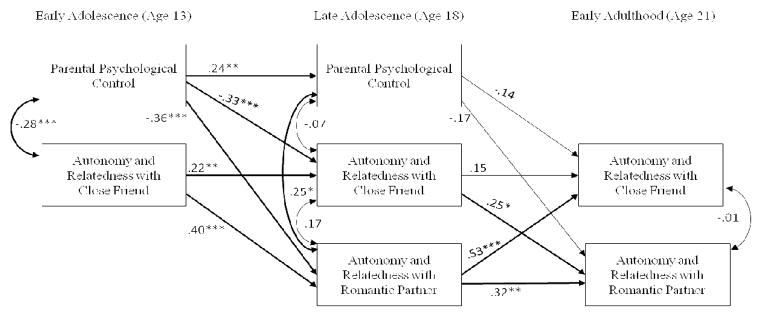
Standardized Solution for the Developmental Cascade Model of Autonomy and Relatedness
Note. Significant pathways are bolded. Significant income pathways were controlled for but not shown in the figure. At age 13, living in lower income households was concurrently significantly associated to greater parental psychological control, r = −0.32, p < .001, and less positive autonomy and relatedness with close friends, r = .29, p < .001. Model fit was good: X2(10) = 4.27, p = .93, RMSEA = 0.00 (90% CI: 0.00–0.02), SRMR = .03. R2= .20, p = .002 and R2= .38, p < .001 for autonomy and relatedness with close friends at age 18 and age 21 respectively, R2= .37, p < .001 and R2= .26, p = .004 for autonomy and relatedness with romantic partners at age 18 and age 21 respectively. *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001.
