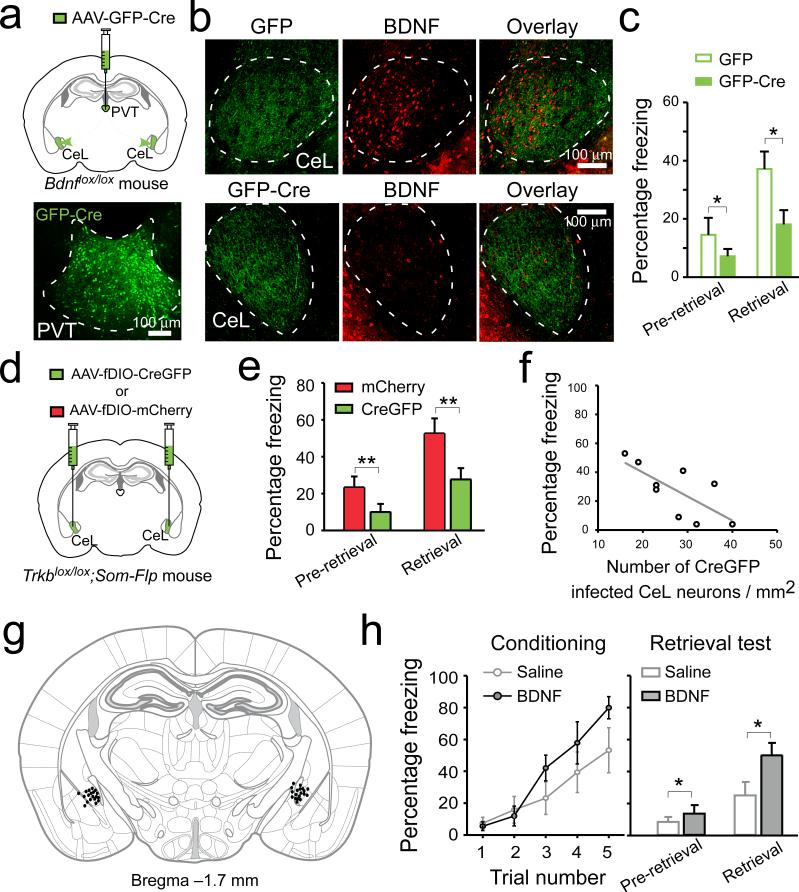
Figure 4. BDNF/TrkB-mediated pPVT–CeL communication is essential for fear conditioning.
a. Top: a schematic of the experimental approach. Bottom: a representative image of pPVT infected with AAV-GFP-Cre. b. Representative images of CeL from Bdnflox/lox mice in which the pPVT was injected with either AAV-GFP (upper panels) or AAV-GFP-Cre (lower panels). Mice injected with AAV-GFP-Cre in pPVT showed marked reduction of BDNF labeling in CeL (middle and right panels). c. Deletion of Bdnf in pPVT significantly reduced freezing levels during memory retrieval test (n = 16 mice for both groups; effect of treatments, F(1,60) = 6.91, P < 0.05; effect of CS presentation, F(1,60) = 11.17, P < 0.01; interaction, F(1,60) = 1.34, P > 0.05; *P < 0.05; two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test). d. A schematic of the experimental approach. e. Selective deletion of Trkb in SOM+ CeL neurons significantly reduced freezing levels during memory retrieval test (n = 9 and 10 mice for CreGFP and mCherry, respectively; effect of treatments, F(1,30) = 9.59, P < 0.01; effect of CS presentation, F(1,30) = 14.37, P < 0.001; interaction, F(1,30) = 0.88, P > 0.05; **P < 0.01; two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test). f. The bilateral infection rate in CeL significantly correlated with freezing levels during retrieval (R2 = 0.44, P < 0.05, n = 9 mice; linear regression is indicated by a gray line). g. Drawing of the cannula sites. Each dot denotes where the tip of the injection cannula was located in each mouse. h. BDNF infusion into CeL promotes fear learning. Left: performance of mice during a mild conditioning procedure (see Methods). BDNF infusion had a trend to improve performance (F(1,55) = 3.65, P = 0.06, two-way ANOVA). Right: BDNF infusion enhanced freezing levels during memory retrieval test (n = 9 and 10 mice for saline and BDNF, respectively; effect of treatment, F(1,34) = 5.63, P < 0.05; effect of CS, F(1,34) = 17.35, P < 0.001; interaction, F(1,34) = 2.44, P > 0.05; *P < 0.05; two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test). Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m.