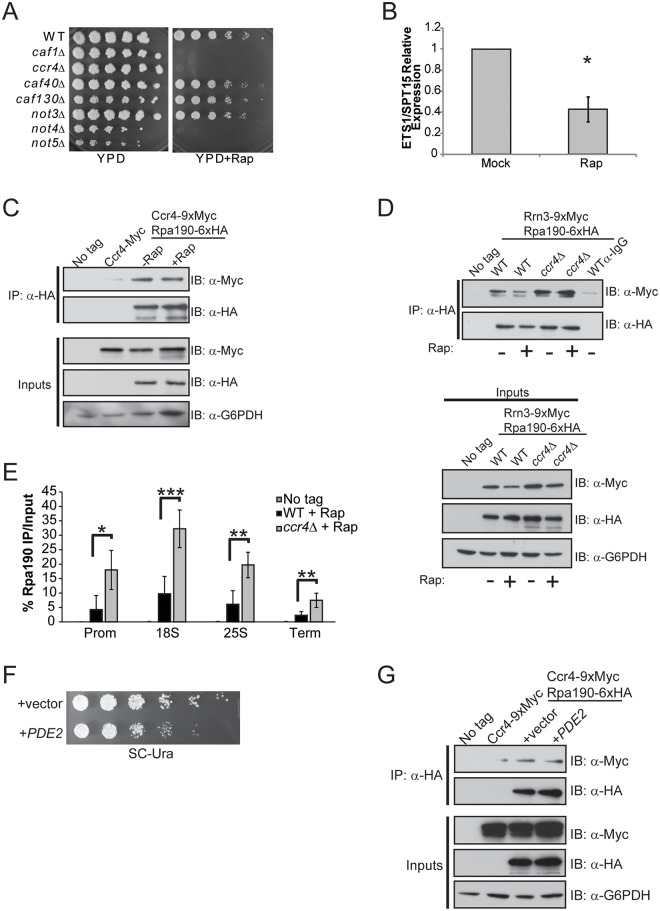
Fig 5. mTORC1 regulation of Rrn3-Pol initiation complex formation depends on functional Ccr4-Not.
(A) Spotting assay of WT and the indicated Ccr4-Not deletion mutants on nutrient rich (YPD) or YPD + 25 nM rapamycin. Plates were incubated at 30°C for four days. (B) Expression of ETS1 in WT cells either mock-treated or treated with 200 nM rapamycin for 30 minutes. The average and SD of three independent experiments are shown. (C) Ccr4-Not association with Pol I is not disrupted when mTORC1 is inhibited. The indicated strains were cultured in YPD before mock treating or treating with 200 nM rapamycin for 30 minutes. Cell extracts were prepared, Pol I was immunoprecipitated and the association of Ccr4 determined by α-Myc immunoblot. Inputs represent 30 μg of total cell extract. (D) mTORC1 down regulation does not disrupt Rrn3-Pol complex formation in ccr4Δ. The indicated strains were cultured and the experiment was performed as in (C). α-IgG indicates negative control immunoprecipitation using extracts from the mock-treated WT sample. The data are representative of three independent experiments. (E) ChIP for Pol I in wild-type and ccr4Δ cells treated with rapamycin as in (D). Data are the average and SD of four independent experiments. (F) The Ccr4-9XMyc/Rpa190-6XHA strain was transformed with control vector or vector overexpressing PDE2. Cells were cultured overnight in SC-leu media and then equal numbers of cells were 5-fold serially diluted and spotted onto a SC-leu plate. The plate was incubated for four days at 30°C. (G) The indicated strains from (F) were cultured in SC-leu media before preparing cell extracts and performing Pol I immunoprecipitations as in (C). Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test. *- p< 0.05; **- p<0.01; ***- p<0.005