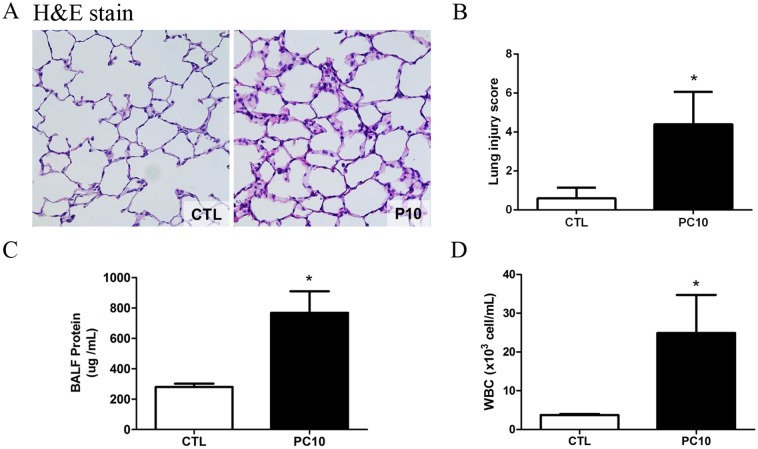
Fig 1. The severity of lung injury was assessed after high-pressure ventilation for 4 hours in each rat.
A: Histology of lung tissue was assessed by hematoxylin and eosin staining. Lung tissue sections are shown by a 400× magnification of representative micrograph. Blue staining indicates nuclei counterstain. PC10: animals ventilated with high pressure at 10 cmH2O; CTL: control group animals without ventilator administration B: The lung injury score was used to represent the severity of lung injury, and was calculated as the sum of the two scores for alveolar wall thickness and neutrophil infiltration per high power field (400× magnification). C: Protein levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were estimated by BCA kit assay. BALF: bronchial alveolar lavage fluid; D: The numbers of white blood cells in BALF stained with Türk solution were calculated by cell counter under light microscope. *:P <0.001 versus animal without ventilator. The data are presented in terms of mean±SEM for the eight rats in each group.