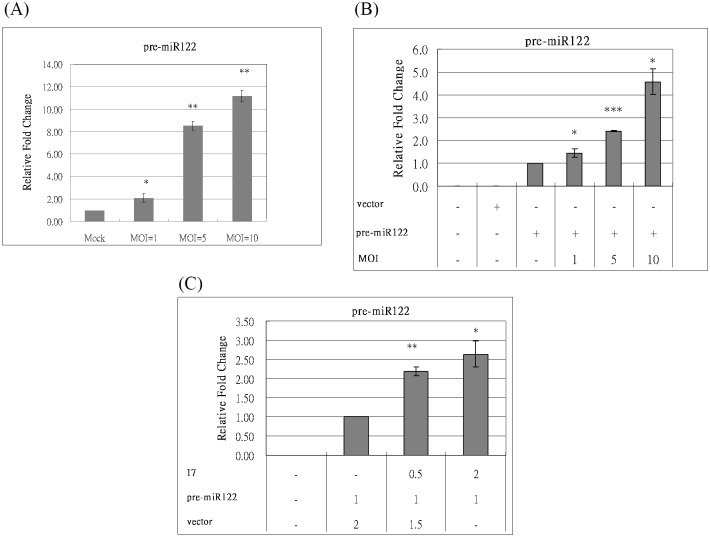
Fig 4. Inhibition of miR122 processing either by VV infection or by I7 protease expression.
(A) HuH7 cells were either mock-infected or infected with VV in different M.O.I. (1, 5, and 10). Twenty-four hrs after infection, mRNAs were extracted and converted into cDNA. Then, real-time PCR assay was performed to detect the amount of miR122 using U6 mRNA as the internal control for normalization. (B) HeLa cells were mock-transfected, transfected with empty vector (2 ug) or with the plasmid expressing pre-miR122 (2 ug). Twenty-four hrs after transfection, the cells with pre-miR122 were mock-infected or infected with VV in different M.O.I. (1, 5, and 10). Twenty-four hrs after infection, mRNAs were extracted and converted into cDNA. Then, real-time PCR assay was performed to detect the amount of miR122 using U6 mRNA as the internal control for normalization. (C) HeLa cells were mock-transfected or co-transfected with the plasmids expressing pre-miR122 and I7 protease with the indicated amount. Forty-eight hrs after transfection, mRNAs were extracted and converted into cDNA. Then, real-time PCR assay was performed to detect the amount of miR122 using U6 mRNA as the internal control for normalization. (p<0.05, *; p<0.01, **; p<0.001, ***).