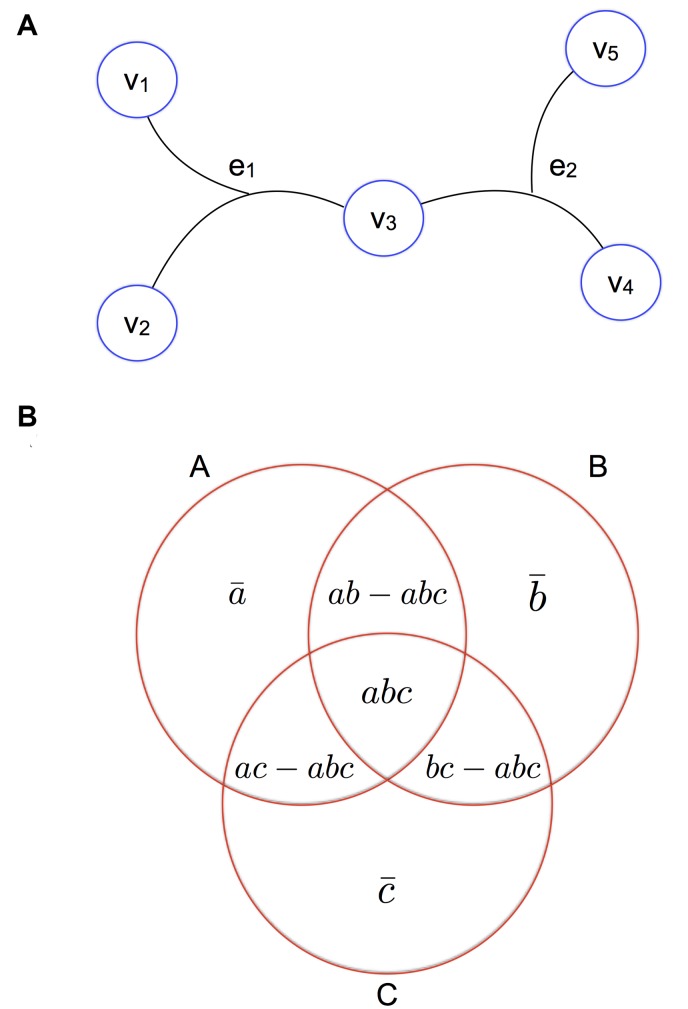
Fig 1. 3-way edges and intersections.
(a) A small, 3-way network consisting of 5 nodes v 1, v 2, v 3, v 4 and v 5 and two 3-way edges e 1 and e 2. Edge e 1 connects nodes v 3, v 4 and v 5 and edge e 2 connects nodes v 1, v 2 and v 3. (b) Venn diagram for a 3-way intersection of species. a is the number of families present in species A, b is the number of families present in species B, c is the number of families present in species C, ab is the number of families present in species A and species B, ac is the number of families present in species A and species C, bc is the number of families present in species B and species C, abc is the number of families present in species A, B and C, is the number of families present only in species A, is the number of families present only in species B and is the number of families present only in species C.