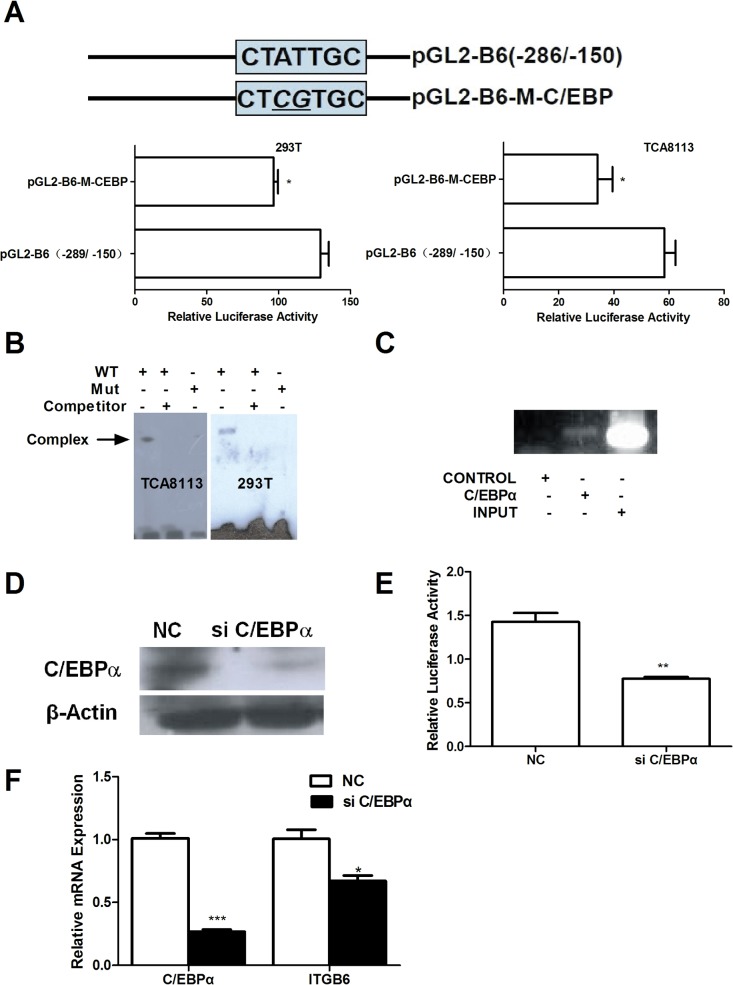
Fig 5. Involvement of C/EBPα in the transcriptional regulation of ITGB6.
(A) Luciferase activity expressed by TCA8113 and 293T cells after transfection with the potential C/EBPα-binding site-directed mutants pGL2-B6-M-C/EBPα and the WT construct pGL2-B6(−289/−150) for 48 hr. * p < 0.05 vs. WT. (B) EMSA was performed to assay TCA8113 and 293T cells′ nuclear extract protein that binding on oligonucleotides containing the C/EBPα-binding site. (C) ChIP assay was performed using anti-C/EBPα antibody or IgG as a control in TCA8113 cells. Input and immunoprecipitated DNA were amplified by PCR using primer pairs covering the C/EBPα-binding site from −289 to −150. (D) TCA8113 cells were transfected with NC or C/EBPα siRNA for 48 hr, and C/EBPα protein was detected by immunoblot analysis. (E) Relative luciferase activity was detected after NC or C/EBPα siRNA and dual luciferase reporter plasmids were transfected into TCA8113 cells for 48 hr. ** p < 0.01 vs. NC siRNA. (E) SAS cells were transfected with NC or C/EBPα siRNA for 48 hr. C/EBPα and ITGB6 mRNA expression were detected by RT-qPCR. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001 vs. NC siRNA.