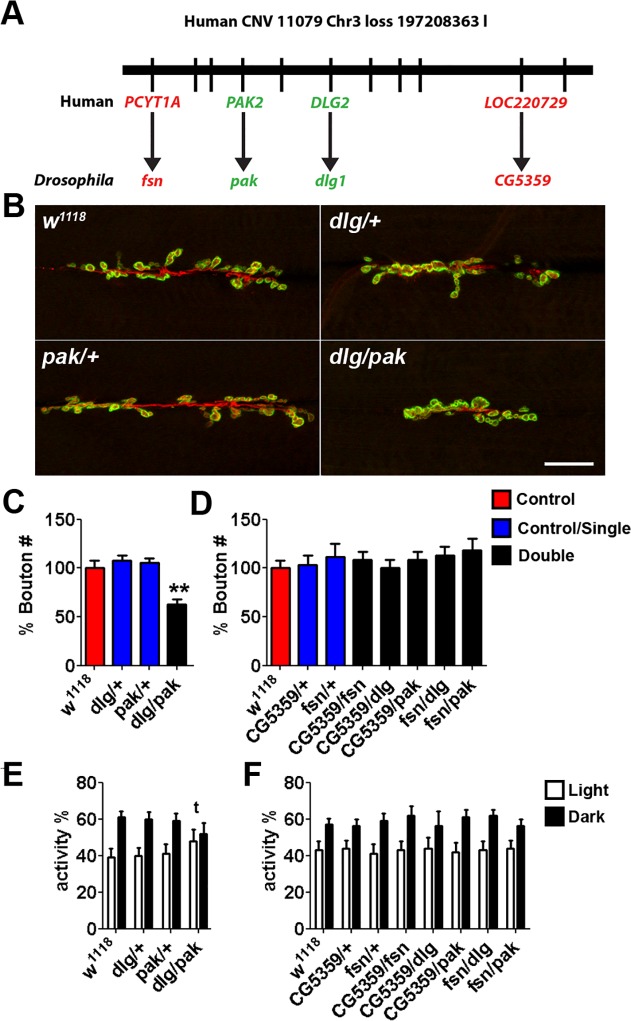
Fig 3. Synergistic interaction in Drosophila between Dlg and Pak, the orthologues of ASD-candidate genes from a de novo loss CNV 11079_chr3_197208363.
A. The Locus of the CNV with mapped Drosophila orthologues (Candidates, green; controls, red). B. Representative pictures of NMJs from dlg/+ (using dlg 1), pak/+ (using pak 6), and dlg/pak 3rd instar larvae; Scale bar = 20μm. C. Synaptic alterations were characterised by NMJ bouton number. Individual heterozygous mutants of candidate gene orthologues dlg and pak (dlg/+ and pak/+) gave no significant change in NMJ morphology over w 1118 controls. However, dlg/pak transheterozygotes have reduced bouton numbers. (n>20, Kruskal-Wallis test, ** P<0.01). D. Non-candidate gene controls fsn (using Fsn KG08128) and CG5359 (using CG5359 e03976) selected from genes found within CNV gave no significant NMJ phenotype singularly or when crossed to form transheterozygotes with dlg or pak. E. and F. Circadian rhythm analysis of candidate genes. All negative control F. and single mutants displayed normal light/dark differences in sleeping patterns. However, transheterozygote dlg/pak flies lost the dark bias, and displayed no significant difference between light/dark sleeping patterns (t).