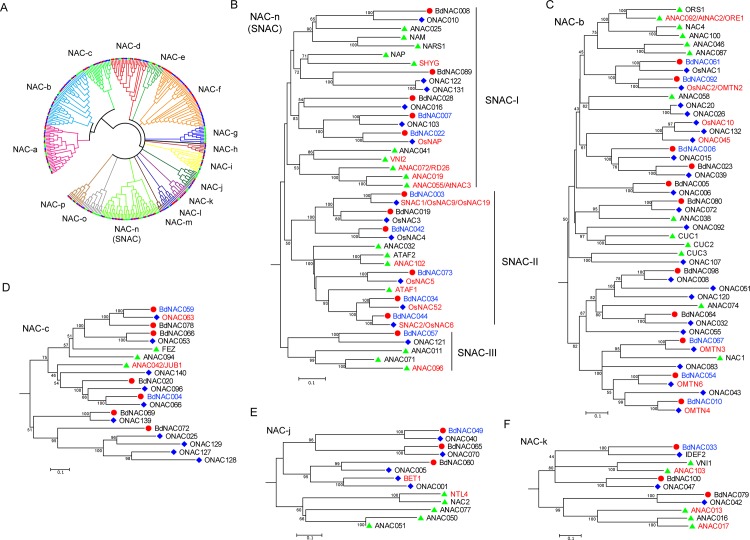
Fig 4. Phylogenetic analysis-based prediction of abiotic stress-related BdNAC genes.
(A). Phylogenetic relationship of NAC proteins from B. distachyon, Arabidopsis and rice. The unroofed phylogenetic tree was constructed using the full-length of 332 NAC proteins from B. distachyon, Arabidopsis and rice by MEGA5. Only the tree topology was presented. The detailed unroofed phylogenetic tree was shown in S6 Fig. (B-F). Clades enriched with stress-related NACs including NAC-n (B), NAC-b (C), NAC-c (D), NAC-j (E) and NAC-k (F). Group NAC-n contains most stress-related NACs (also named it as SNAC), and can be further divided into three subgroups (SNAC-I, SNAC-II and SNAC-III). NAC proteins from B. distachyon, Arabidopsis and rice were denoted by red circle, green triangle and blue diamond, respectively. Known stress-responsive NAC genes from Arabidopsis and rice were indicated in red. Putative stress-related BdNAC genes based on phylogenetic analysis were indicated in blue.