Fig. 2.
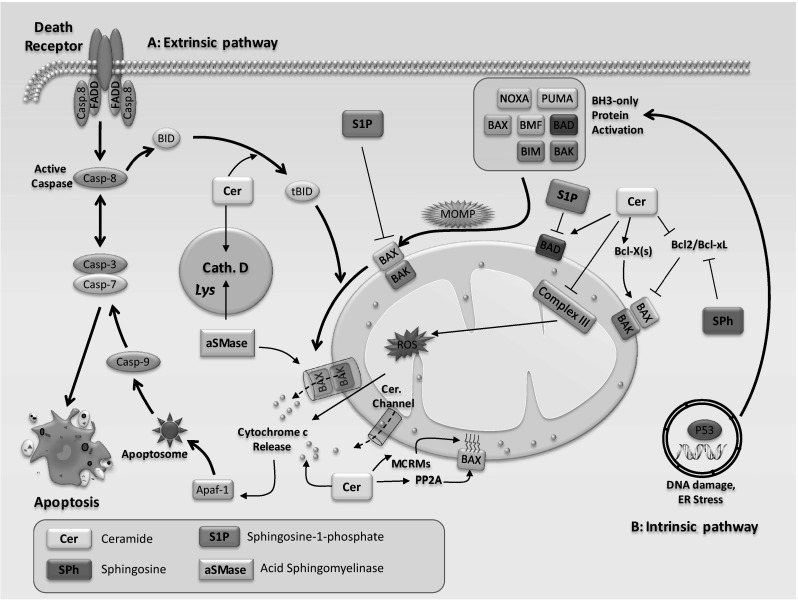
Schematic representation of key events in the apoptotic pathway and regulation of apoptosis by sphingolipids. There are two main apoptotic pathways. A Extrinsic pathway is triggered when cell death ligands (e.g., FasL, APO-2L, TRAIL, TNF) bind to their respective death-receptors (e.g., Fas, DR4, DR5, TNF-R1) and initiates pro-caspase-8 activation by recruiting FADD. Activation of caspase-8 results in cleavage of effector caspases, such as caspase-3,-6,-7, which are involved in the core apoptosis pathway. Furthermore, caspase-8 can truncate BID (tBID), which later induces the intrinsic pathway. B The intrinsic pathway can be directly initiated by a variety of stress signals. Stress signals initiate DNA damage and p53 phosphorylation, which leads to the up-regulation of BH3 only proteins and consequently results in mitochondrial translocation and oligomerization of BAX/BAK, followed by MOMP. Mitochondrial damage leads to cytochrome c release into the cytoplasm. Cytosolic cytochrome c binds to the pro-apoptotic factor Apaf-1 (in the presence of dATP) to form an apoptosome. Apoptosomes then activate caspase-9, which later leads to the activation of caspases-3 and-7, and subsequently to nuclear fragmentation and also chromatin condensation. Sphingolipids have been shown to modulate apoptosis at multiple steps of the process. Sphingolipids may directly affect mitochondria, a strategic center in the control of apoptosis. Ceramide forms channels in mitochondrial outer membranes and promotes the release of cytochrome c for caspase-9 activation. Ceramide channel formation has also shown to be inhibited by dihydroceramide. Furthermore, ceramide generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) via inhibition of mitochondrial complex III. The apoptotic action of ceramide could also be mediated by the recruitment and activation of pro-apoptotic Bax at the mitochondria through the PP2A-dependent dephosphorylation of Bax and formation of mitochondrial ceramide-rich macrodomains (MCRMs). aSMase-released ceramide binds directly to lysosomal protease cathepsin D, leading to cathepsin D activation, resulting in cleavage of the BH3-only protein BID and induction of the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Sphingosine has been shown to downregulate expression of anti-apoptotic proteins, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, to enhance apoptosis. While ceramide-mediated activation of pro-apoptotic protein, BAD, promotes apoptosis, S1P suppresses apoptosis via BAD inactivation
