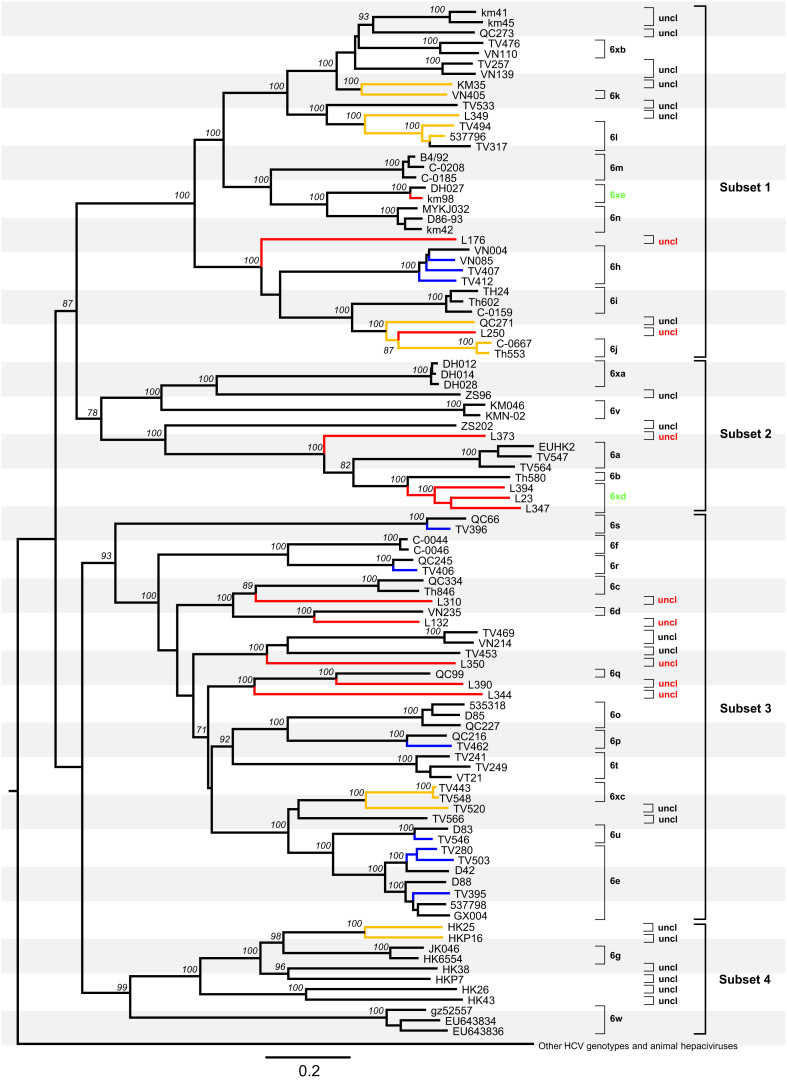
Fig. 1.
Maximum likelihood tree obtained for 110 full-length HCV genome sequences. The 22 new genomes obtained in this study are in blue (subtypes 6e, 6h, 6p, 6r, 6s, and 6u) or red (new subtypes 6xd, 6xe, and eight unclassified variants). They were analyzed together with 77 HCV-6 full-length references and 11 references from the other six genotypes and 15 sequences of animal hepciviruses. The latter 11 and 15 sequences have been compressed into a single outgroup for clarity. Yellow branches indicate those sequences whose pairwise nucleotide differences fall within a range of 13.5–15%. Subtypes, unclassified lineages, and four subsets discussed in the main text are labelled on the right hand side each. Two new subtypes 6xd and 6xe and eight newly identified unclassified lineages are indicated in green and red, respectively. All others are all indicated in black. Bootstrap supports values >70% are shown in italics at internal nodes, and the scale bar beneath the tree represents 0.10 nucleotide substitutions per site.