Figure 2.
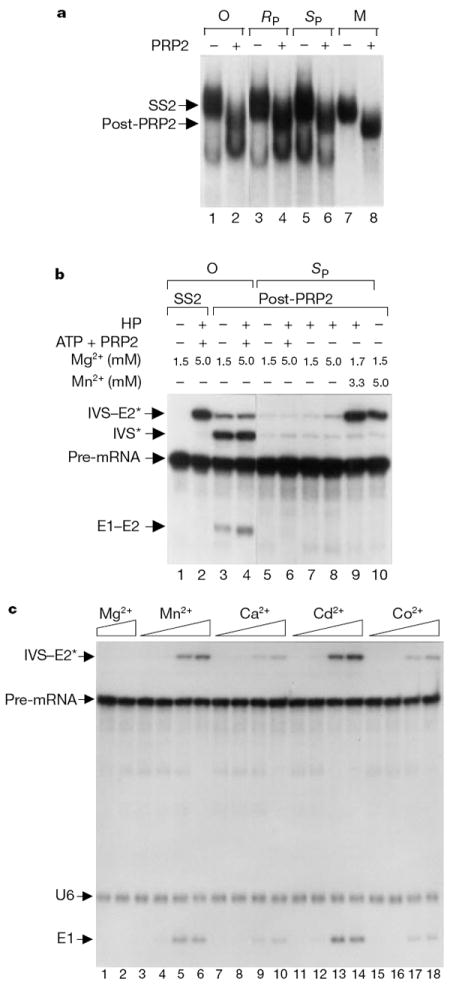
Spliceosome maturation is not affected by phosphorothioate substitution at U80 of U6 but splicing only occurs in the SP diastereomer with a thiophilic metal ion. a, U6/sU80 forms mature spliceosome. Extracts were reconstituted with unmodified U6 (lanes 1 and 2) or U6/sU80 (RP, lanes 3–4; SP, lanes 5–6), in the absence (lanes 1, 3 and 5) or presence (lanes 2, 4 and 6) of PRP2. The reaction mixture was sedimented through a glycerol gradient and the fraction containing the spliceosome was analysed on a native gel. The pre-catalytic and post-PRP2 spliceosomal markers (M; lanes 7 and 8) were generated as described16. b, The first transesterification reaction occurs in U6/sU80(SP)-containing post-PRP2 spliceosome in the presence of Mn2+. Spliceosomes isolated from glycerol gradients were incubated in buffer containing combinations of Mg2+, Mn2+, ATP, PRP2 and HP (a protein factor that facilitates splicing in purified spliceosomes16). c, Other thiophilic divalent metal ions can also rescue the transesterification reaction. The post-PRP2 U6/sU80(SP) spliceosome was incubated with metal ions without the addition of ATP, PRP2 or HP. Mg2+ was added as the sole divalent metal ion in lanes 1 (2.5 mM) and 2 (5 mM). The concentrations (mM) of the thiophilic metal (Mn2+, Ca2+, Cd2+ or Co2+) in each set were 0.02, 0.1, 0.5 and 2.5. Mg2+ was added to lanes 3–18 to make the total concentration of divalent metal ions 5 mM.
