Figure 3. Protein sequence alignment of vertebrate MGAT and DGAT2 and predicted insect MGATs.
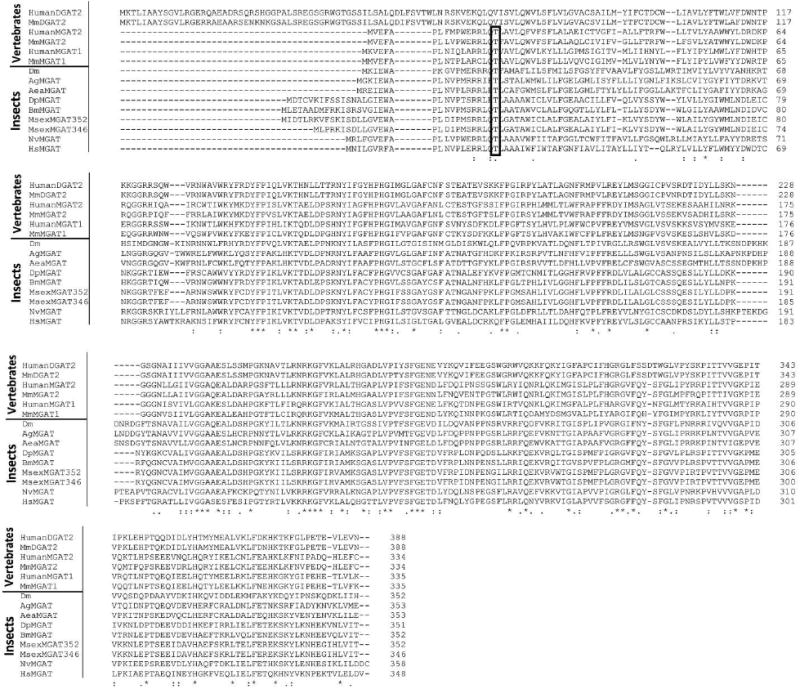
Sequence identifiers for DGAT2 proteins: HumanDGAT2: Q96PD7; MmDGAT2: Mus musculus DGAT2, NP_080660.1.
Sequence identifiers for MGAT proteins: HumanMGAT1: Homo sapiens MGAT1 NP_477513.2; MmMGAT1: Mus musculus MGAT1, NP_080989.2; MmMGAT2: Mus musculus MGAT2, Q80W94; HumanMGAT2: Homo sapiens MGAT2, NP_079374.2; DpMGAT: Danaus plexippus EHJ64327.1; ; MsexMG352: Manduca sexta MGAT2 (352aa) KF800700; MsexMG346: Manduca sexta MGAT2 (346aa) KF800699; BmMGAT: Bombyx mori XP_004922894.1 Dm: Drosophila melanogaster CG1941; AgMGAT: Anopheles gambiae EDO63767.1; AeaMGAT: Aedes aegypti AAEL008878-PA; NvMGAT: Nasonia vitripennis XP_001602288.1; HsMGAT: Harpegnathos saltator, EFN85928.1.
The rectangle encloses a conserved threonine residue that is a probable PKA phosphorylation site. It is only conserved among MGAT proteins.
