Fig. 1.
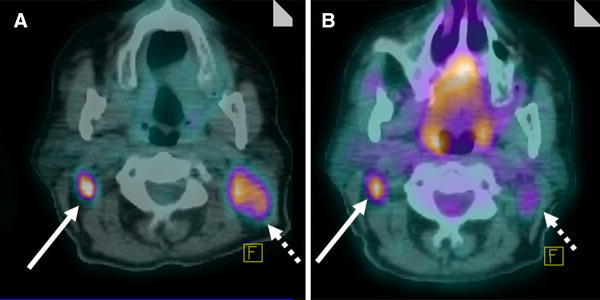
Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography (FDG PET-CT) images. This patient had lymph node metastatases from a planocellular nasopharyngeal carcinoma of the right neck (solid arrow) coexisting with Hodgkin lymphoma at the left neck (dotted arrow). a Pretreatment FDG PET-CT scan showed pathological FDG uptake at the carcinoma and lymphoma. b The FDG PET-CT scan after two cycles of chemotherapy (cisplatin, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide) showed a partial metabolic response of carcinomatous localisation (maximum standardised uptake value [SUVmax], −54 %; total lesion glycolysis, −47 %) and complete metabolic regression of lymphomatous localisation (SUVmax, −69 %; total lesion glycolysis, −82 %; downshifted from Deauville 4 to Deauville 2)
