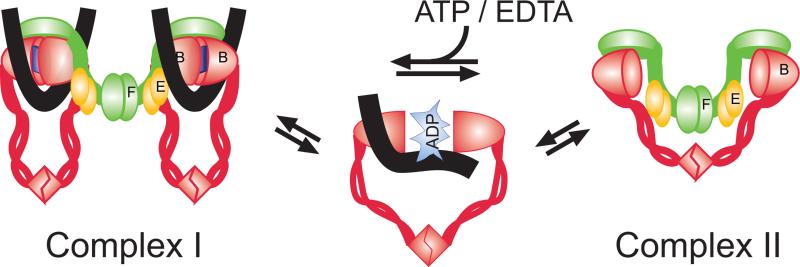
Figure 4.
A schematic view on ATP-mediated regulation of DNA binding and architecture of MukBEF. ATP binding promotes engagement of MukB heads, which creates a high affinity DNA binding site and is accompanied bybinding of DNA (black lines) and formation of the MukB2-Muk(E2F) complex (Complex I). ATP hydrolysis promotes dissociation of the heads (or perhaps another functionally identical conformational change), which disrupts the DNA binding site and forces dissociation of DNA and promotes formation of the MukB2-Muk(E2F)2 complex (Complex II).