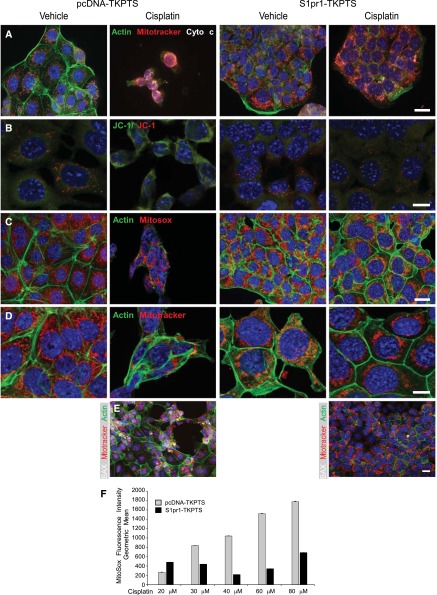
Figure 5.
Overexpression of S1P1 protects TKPTS cells from cisplatin-induced cell death and mitochondrial injury. TKPTS cells were stably transfected (and maintained under G418 selection) with control pcDNA3.1 vector (pcDNA-TKPTS) or vector containing the sequence for S1p1r (S1pr1-TKPTS). Cells were incubated with vehicle (saline) or cisplatin (20 μM) for 24 hours and then were labeled with various combinations of cell and mitochondrial markers. (A) FITC-phalloidin to label actin (green), MitoTracker (red), cytochrome c (white). Overlay of red MitoTracker and white cytochrome c appears pink in merged images. (B) Membrane potential–sensitive red/green JC-1 is green in the cytoplasm and red within mitochondria with high membrane potential. (C) FITC-phalloidin (green) and MitoSox Red, which fluoresces more brightly with increasing mitochondrial superoxide. (D) FITC-phalloidin (green) and MitoTracker (red) showing mitochondrial morphology. (E) BAX labeling (white) appears white to pink upon translocation to and overlay with mitochondria (MitoTracker, red). Blue, nuclei stained with DAPI. (F) Mean fluorescence intensity of MitoSox Red in cells incubated with increasing concentrations of cisplatin for 24 hours and analyzed by flow cytometry. Flow histograms from a representative experiment are shown in Supplemental Figure 5. n=3 and the experiment was repeated two times. Bar, 20 μm in A, C, and E; 10 μm in B and D.