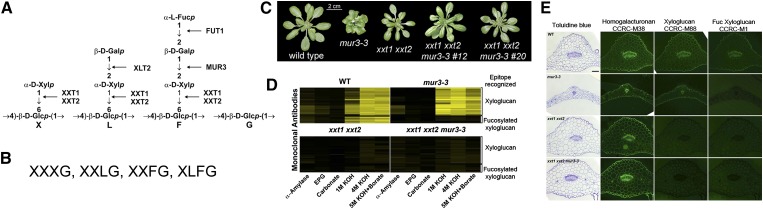
Figure 1.
Eliminating xyloglucan suppresses the cabbage-like phenotype of mur3-3 plants. A, The major structural features of Arabidopsis XyG and the glycosyltransferases required for side chain formation. Side chains are represented by the letters X, L, and F. An unbranched Glc is designated by the letter G. B, The predominant subunits of Arabidopsis XyG. C, Eliminating XyG suppresses the dwarf phenotype of the mur3-3 mutant. mur3-3 was crossed with xxt1 xxt2, and two independent xxt1 xxt2 mur3-3 triple mutants (nos. 12 and 20) were identified by reverse transcription (RT)-PCR. Plants were grown with a 14-h-light (19°C) and 10-h-dark (15°C) cycle. D, The glycome profiles of the materials solubilized from the cell walls by enzymatic and KOH treatments. Each extract was probed with a series of monoclonal antibodies that recognize epitopes of XyG irrespective of the presence or absence of fucosylated side chains and monoclonal antibodies that bind only to XyG containing fucosylated side chains. Yellow, Strong binding; black, no binding. No XyG was detected in the xxt1 xxt2 double mutant or the xxt1 xxt2 mur3-3 triple mutants. E, Cross sections of wild-type and mutant leaves stained with toluidine blue (left column) or immunolabeled with monoclonal antibodies that recognize epitopes of deesterified homogalacturonan (CCRC-M38), XyG (CCRC-M88), or fucosylated XyG (CCRC-M1). WT, Wild type; EPG, endopolygalacturonase.