Figure 5.
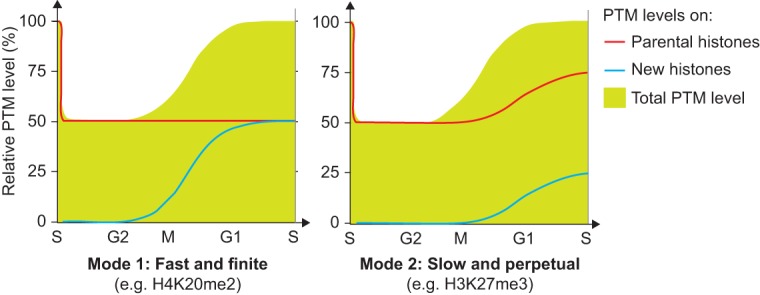
Illustration of the two basic principles for histone PTM propagation. The contribution of new and parental histones (lines) to the total PTM level (green) is shown. (Mode 1) New histones acquire PTMs to become identical to the parental histones within one cell cycle (H3K9me1, H3K27/36me1, H3K36me2, H3K9me2, H3K27me2, H3K79me1, H3K79me2, H4K20me1, and H4K20me2); (Mode 2) propagation relies on progressive modification of both new and parental histones (H3K9me3 and H3K27me3).
