Figure 1.
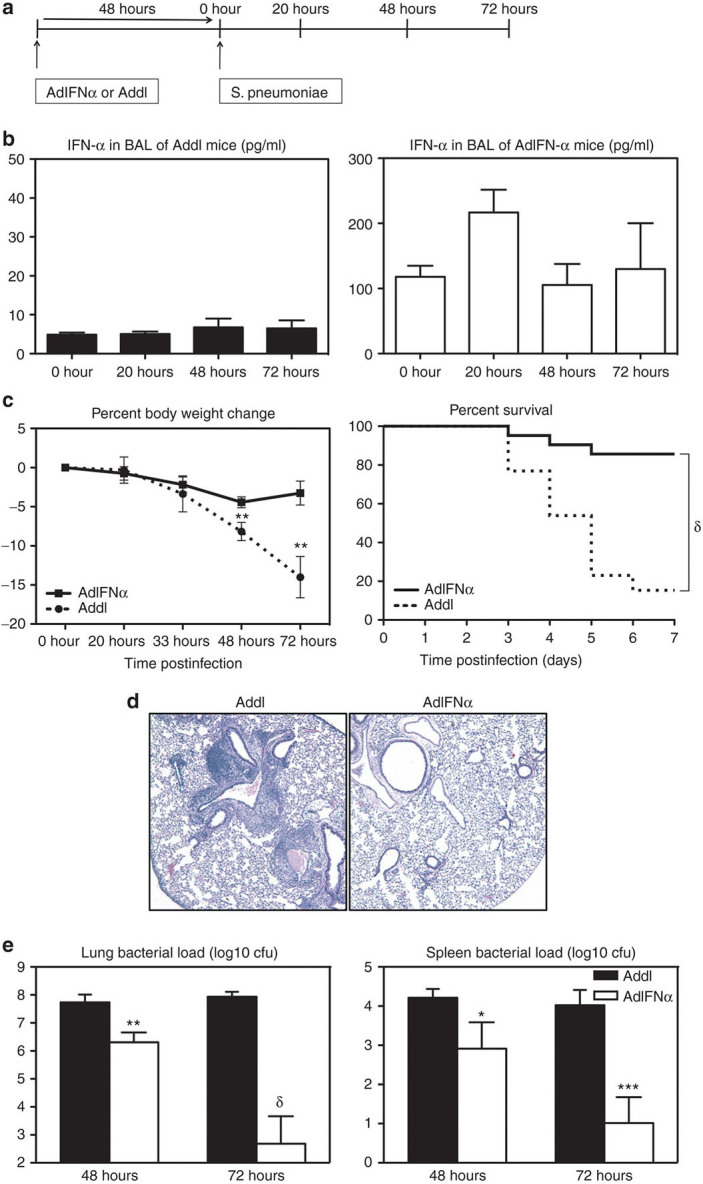
Transgenic expression of interferon (IFN)-α improves clinical outcome and bacterial control following pneumococcal infection. (a) Experimental schema. Female C57BL/6 mice were infected with 107 plaque-forming units (pfu) AdIFN-α or Addl and 48 hours later with 104 colony-forming unit (cfu) of S. pneumoniae. (b) IFN-α was measured in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) 48 hours after infection with Ad (0-hour time point) and at 20-, 48-, 72-hour post-Strep by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Results are from two to four independent experiments, n = 4–10/group. (c) Average percent body weight change and survival were monitored (end point was considered as 20% body weight loss; log-rank test, P < 0.0001). Results are from two to six independent experiments, n = 10–44/group/time point. (d) Histopathological changes in the lung were examined by hematoxylin and eosin staining at 72-hour post-Strep infection (magnification ×5). (e) Lung and spleen bacterial load was measured using a colony forming unit (CFU) assay at 48- and 72-hour post-Strep infection. Results are from three independent experiments, n = 5–8/group/time point. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005, δ, P < 0.0005.
