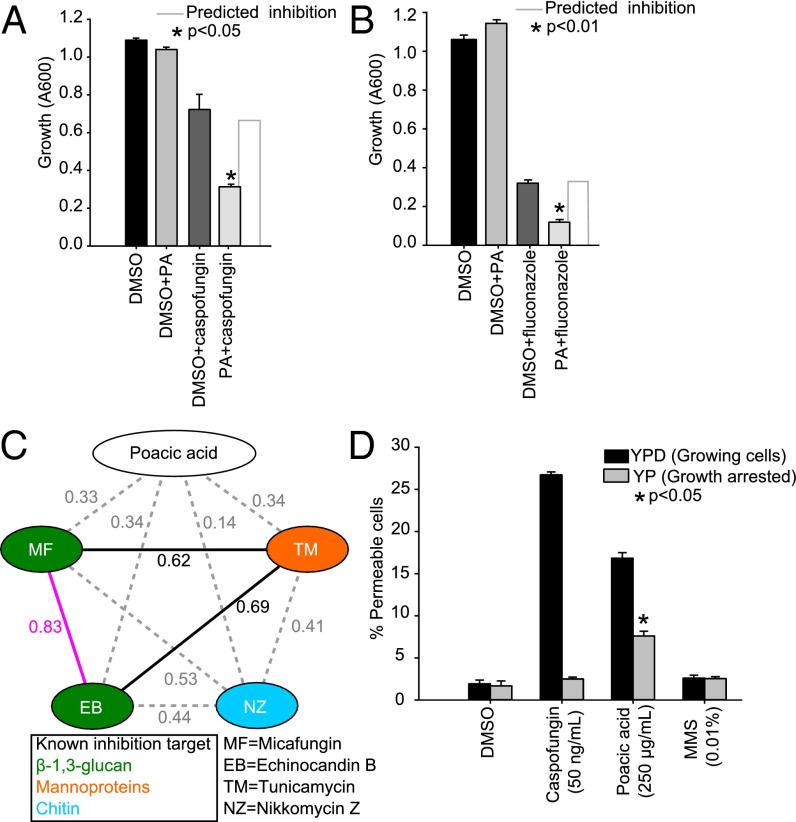
Fig. 4.
Synergisms and the mode of action of poacic acid. (A) Poacic acid (125 µg/mL) is significantly synergistic with caspofungin (12.5 ng/mL). (B) Poacic acid (125 µg/mL) is also synergistic with fluconazole (3.8 µg/mL). (C) Morphological similarity between poacic acid and other cell wall-affecting agents was measured based on the correlation coefficient value (R) of their morphological profiles. (D) Poacic acid causes cell leakage within 4 h of treatment, similar to the cell wall-targeting compound caspofungin. The leakage is most apparent in actively growing cells [yeast extract peptone dextrose (YPD)] compared with cells arrested without a carbon source [yeast extract peptone (YP)]. DMSO and MMS were included as control agents that do not directly affect cell wall integrity. In arrested cells, poacic acid had significantly greater cell leakage than other treatments. One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test were used to calculate the differences between treatments (mean ± SE). PA, poacic acid.