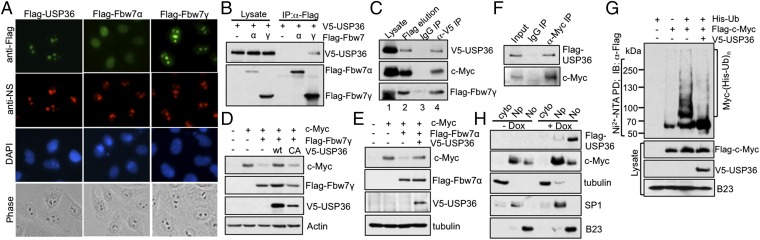
Fig. 3.
USP36 interacts with Fbw7γ, but not Fbw7α; inhibits c-Myc degradation mediated by either Fbw7γ or Fbw7α; and deubiquitinates c-Myc in the nucleolus. (A) Immunofluorescence (IF) staining. HeLa cells transfected with Flag-USP36, Flag-Fbw7γ, or Flag-Fbw7α were immunostained with anti-Flag (green) and anti-nucleostemin (NS) (red). (B) USP36 interacts with Fbw7γ, but not Fbw7α. HeLa cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were assayed by co-IP. (C) USP36 forms a complex with c-Myc and Fbw7γ. HeLa cells transfected with Flag-Fbw7γ, V5-USP36, and c-Myc were subjected to IP with anti-Flag, followed by elution with the Flag peptide. The elution was then subjected to co-IP with control IgG or anti-V5. (D and E) USP36 inhibits c-Myc degradation mediated by Fbw7γ or Fbw7α. HeLa cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were assayed by IB. (F) USP36 interacts with c-Myc in the nucleolus. The nucleolar fraction isolated from HeLa cells expressing Flag-USP36 as in Fig. S3E was assayed by co-IP. (G) USP36 deubiquitinates c-Myc in the nucleolus. The nucleoli isolated from HeLa cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were assayed by Ni2+-NTA PD. (H) Overexpression of USP36 increases the levels of c-Myc in both the nucleoplasm and the nucleolus. HeLa–TO (tetracycline operator)–Flag-USP36 cells were induced without or with doxycycline (dox) for 12 h and assayed by cell fractionation and IB.