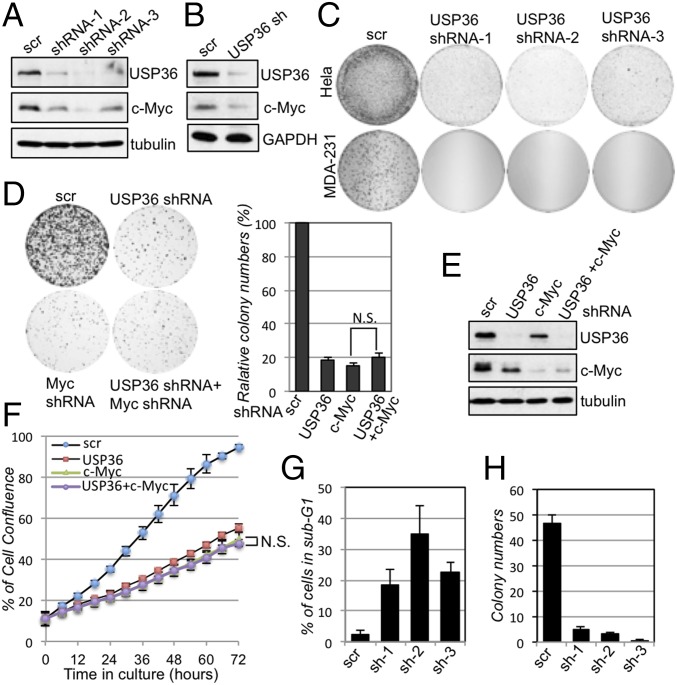
Fig. 4.
Knockdown of USP36 reduces c-Myc levels and suppresses cell proliferation. (A and B) Knockdown of USP36 reduces c-Myc levels. HeLa (A) and MCF10A (B) cells were infected with scrambled or USP36 shRNA-encoding lentiviruses. The cell lysates were assayed for the expression of c-Myc and USP36 by IB. (C) Knockdown of USP36 suppresses cell proliferation. HeLa or MDA-MB-231 cells were infected with control or USP36 shRNA-encoding lentiviruses. The cells were cultured for up to 3 wk. The colonies were visualized by staining with crystal violet. (D–F) Knockdown of c-Myc does not further increase the inhibitory effects of knockdown of USP36 on cell proliferation. HeLa cells infected with control, USP36 shRNA, or c-Myc shRNA-encoding lentiviruses alone or together were subjected to colony formation assay (D) or measurement of cell confluence over time using IncuCyte System (F). A representative IB detection of the expression of USP36 and c-Myc is shown in E. (G) Knockdown of USP36 induces apoptosis. HeLa cells infected with control or USP36 shRNA-encoding lentiviruses were stained with propidium iodide (PI) followed by flow cytometry analysis. The average percentages of cells in sub-G1 are shown. (H) Soft agar colony formation assays. MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines were infected with control or USP36 shRNA-encoding lentiviruses, followed by colony formation assay in soft agar.