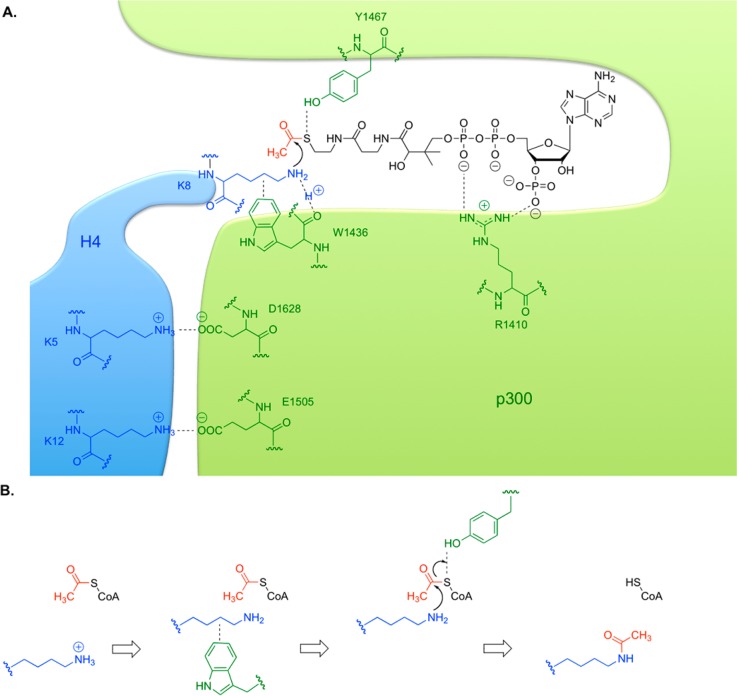
Figure 7.
Acetyl transfer catalysis by p300. (A) The p300 active site is drawn in green, and histone H4 substrate in blue, with important residues indicated. CoA is drawn in black, and binds in a specific tunnel. (B) Four steps in a proposed p300 mechanism. acetyl-CoA binds, then peptidyl-lysine binds. The hydrophobic indole of W1436 promotes an uncharged lysine and positions it for attack. The lysine attacks the carbonyl of acetyl-CoA, while Y1467 acts as a general acid to protonate the leaving group. Acetyl-lysine-containing product leaves quickly, then CoASH departs slowly.