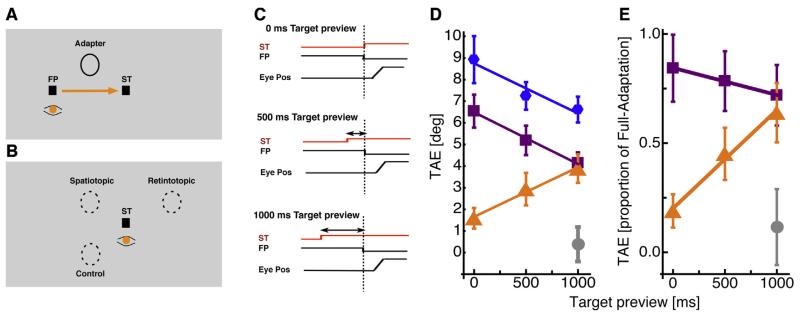
Fig. 1.
(A) Graphical illustration of setup used to study spatiotopy with adaptation. Subjects fixated loosely on the fixation point FP for 3000 ms, viewing an adapter grating patch (0.8 c/°, vignetted within Gaussian window of σ = 3.5°) tilted at +15° or −15°. The saccade target (ST) was then presented, to which subjects saccaded on extinction of the fixation point: either at onset of the saccade target, or 500 or 1000 ms later. (B) The test target came on 300 ms after extinction of the fixation point, always at least 30 ms after the eyes had landed. 300 ms after extinction of fixation point the test patch was presented for 51 ms in the spatiotopic, the retinotopic, or the control position, and subjects indicated the direction of tilt of the test patch. (C) Timecourse of events in a trial for all target preview durations. In the 0 ms target preview duration condition the saccade target appeared simultaneously with fixation point offset. In the other two conditions the saccade target was shown either 500 ms or 1000 ms before fixation point offset. (D) Tilt-aftereffect for the full-adaptation (blue), retinotopic (purple), spatiotopic (orange) and control (gray) conditions, as a function of preview duration of the saccade target, averaged over all subjects. Error bars represent ±1 SEM. (E) Normalized tilt-aftereffect results for the three eye-movement conditions (color-coding as for B). Aftereffect magnitude was divided by each subject’s full-adaptation magnitude, then averaged over subjects. Error bars represent ±1 SEM. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of the article.)