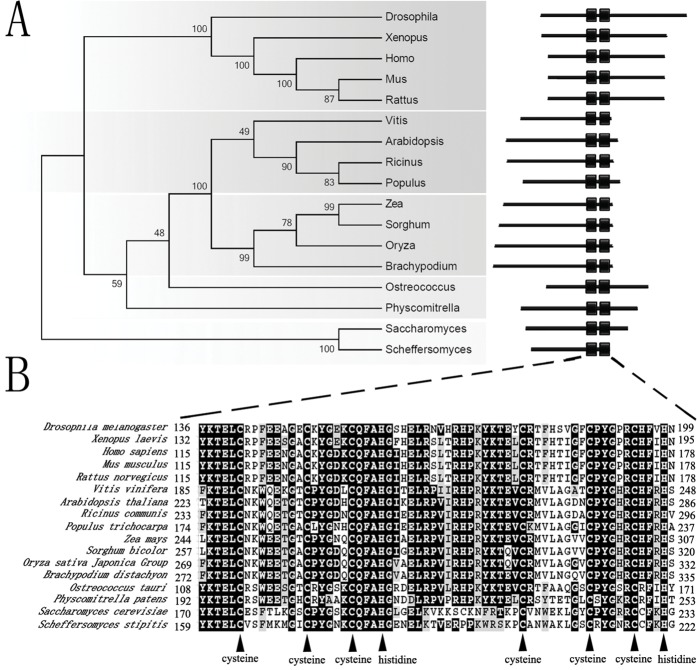
Fig 1. Phylogenetic analysis of AtTTP and orthologous proteins.
(A) Unrooted phylogenetic tree of NPU and its orthologous proteins. The protein sequences of AtTTP and its orthologs were analyzed with the neighbor-joining method by MEGA5.05 software. The numbers at the nodes represent the percentage bootstrap values based on 1,000 replications. The CCCH domains were predicted by the Pfam 26.0 tool online. The protein sequence files are as follows: Drosophila: NP_511141.2; Xenopus: NP_001080610.1; Homo: NP_004917.2; Mus: NP_031590.1; Rattus: NP_058868.1; Vitis: XP_002281139.1; Arabidopsis: NP_176987.1; Ricinus: XP_002526299.1; Populus: POPTR_0010s12860.1; Zea: NP_001148404.1; Sorghum: XP_002440301.1; Oryza: NP_001056400.1; Brachypodium: XP_003569444.1; Ostreococcus: XP_003078184.1; Physcomitrella: XP_001783282.1; Saccharomyces: NP_013237.1; Scheffersomyces: XP_001385679.1. (B) Multiple alignments of AtTTP and its orthologs. Black triangles, the critical CCCH zinc finger residues: Cysteine and histidine.