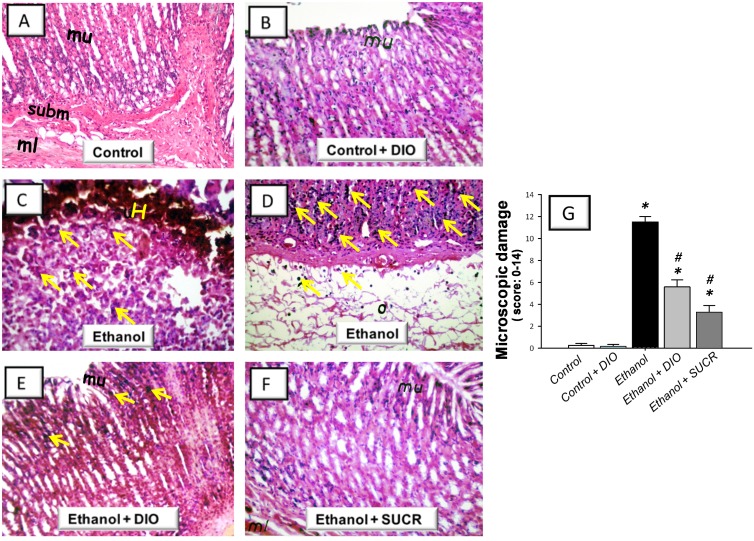
Fig 2. Diosmin alleviates ethanol-induced gastric histopathologic injury in rats.
Representative photomicrographs of sections from gastric wall samples taken 1 h post ethanol administration. (A) Control rats receiving saline vehicle showed normal architecture of mucosa (mu) with intact epithelial surface, submucosa (subm) and muscularis (ml) layers. (B) Control rats receiving DIO (100 mg/kg p.o.) elicited no histologic modifications. (C, D) Ethanol-treated group was characterized by mucosal lesions with marked hemorrhage (H).The mucosa was also infiltrated by inflammatory cells (arrows) that also extended to the submucosa which also displayed extensive edema (o). (E) Ethanol + DIO pretreatment (100 mg/kg p.o.) revealed attenuated morphological modifications, diminished inflammatory cell invasion (arrows) and mucosal preservation. (F) Ethanol + SUCR (100 mg/kg p.o.) pretreatment preserved the architecture of the gastric wall. Hematoxylin and eosin staining, original magnification: × 40. (G) Microscopic damage scores (expressed as median; n = 6–8).