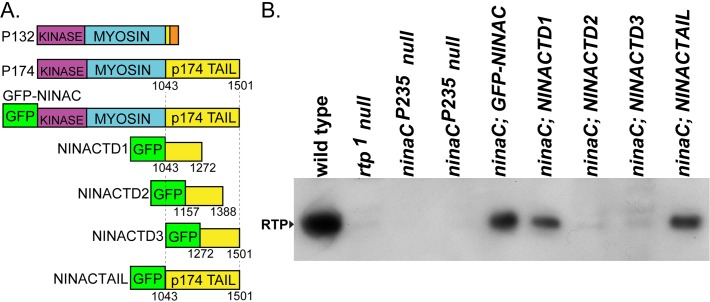
Fig 1. The proximal tail region of NINAC mediates RTP stabilization.
(A) The two upper left entries are a diagram of the P132 and P174 NINAC proteins, indicating the location of the shared kinase and myosin head domains and the distinctive tail domains. In orange is the region unique to P132. The GFP-NINAC construct creates GFP fused to the N-terminus of the full length NINAC protein (not shown). The GFP-NINAC fusion proteins used in this study are diagrammed below P132 and P174 NINAC. These constructs contain GFP fused at the N-terminus of NINACTD1 (= Tail Domain 1, etc.), NINACTD2, NINACTD3 and NINACTAIL proteins. Numbers indicate the first and last NINACp174 amino acid present in these fusion proteins. (B) Protein blot showing the capability of the GFP-NINAC, NINACTD1, and NINACTAIL proteins, but not NINACTD2 and NINACTD3 proteins, to support RTP expression within photoreceptors. The four lanes on left are control genotypes.