Table 3.
Pd-catalyzed and NOx-mediated aerobic acetoxylation of benzene: Optimization of turnover numbers.
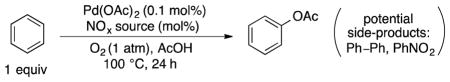
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Entrya | % NOx | TON (Pd)b | PhOAc:PhNO2c |
| 1 | 30% t-BuONO | 4 | 4:1 |
| 2 | 30% NaNO3 | 59 | 9:1 |
| 3 | 30% aq. HNO3 (70%) | 115 | 25:1 |
| 4d | 30% fuming HNO3 | 136 | 26:1 |
| 5 | 10% fuming HNO3 | 100 | 29:1 |
| 6 | 50% fuming HNO3 | 127 | 22:1 |
| 7 | 70% fuming HNO3 | 116 | 18:1 |
| 8 | 30% fuming HNO3; N2 (1 atm) instead of O2 | 19 | 1:1.2 |
| 9e | 30% fuming HNO3, 85 °C, air (1 atm) instead of O2 | 120 | 40:1 |
1.2 mmol scale; 0.55 M. Reactions were conducted in sealed pressure tubes with teflon caps. Biphenyl is not observed.
TONs were calculated based on calibrated GC yields of PhOAc.
Based on the ratio of calibrated GC yields.
Average of four experiments. Standard deviation for TON: 9.9. Standard deviation for ratio of PhOAc:PhNO2: 3.3
13.56 mmol scale; 0.55 M. Reaction was conducted in a flask equipped with a reflux condenser. Biphenyl is not observed.
