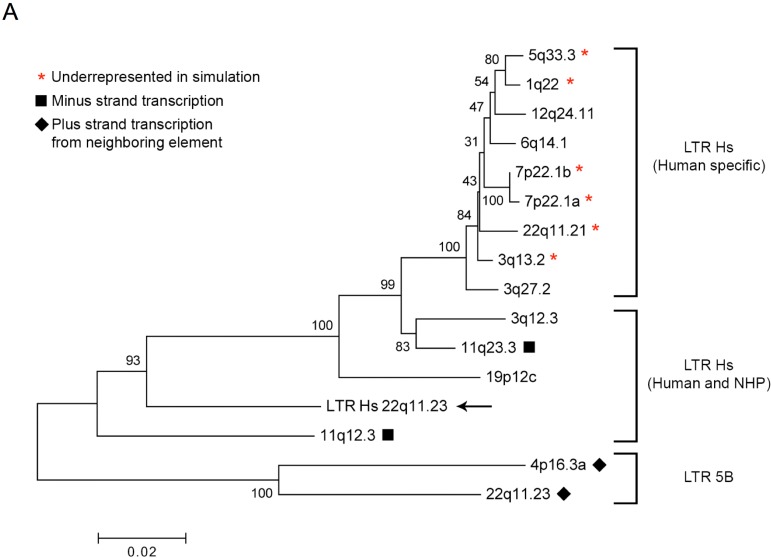
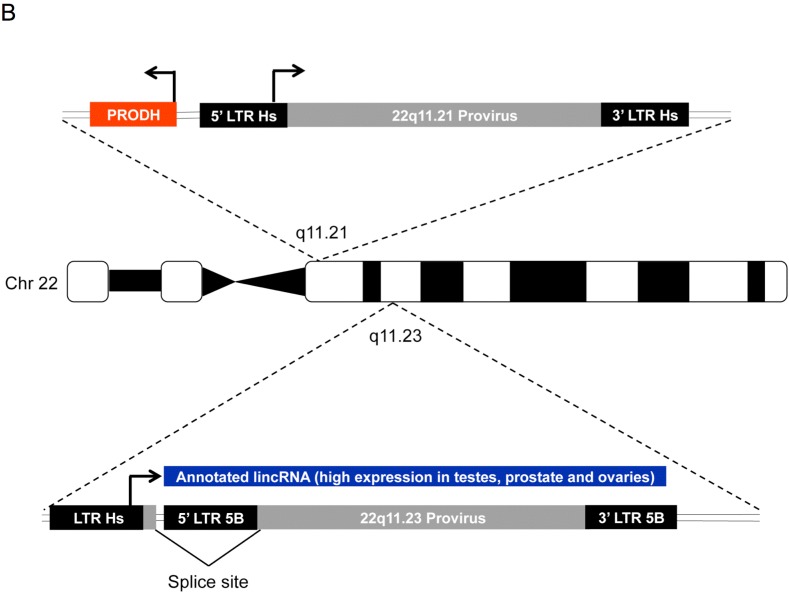
Figure 4.
Transcription of HML-2 proviruses is driven by the native LTR or a nearby element. (A) Neighbor-joining tree of the 5’ LTR sequences of the HML-2 proviruses expressed in Tera-1 cells. The p-distance method was used to calculate distance and bootstrap values are indicated (1000 replicates). Proviruses with (*) were predicted to be underrepresented by the in silico analysis, as in Figure 1. Solid squares (∎) indicate those proviruses (11q23.3 and 11q12.3) with minus strand transcription. Solid diamonds (♦) indicate those proviruses (4p16.3a and 22q11.23) with plus strand transcription, but which appear to originate from a neighboring transcription unit and not the corresponding 5’ LTR. (B) A cartoon of two proviruses located on chromosome 22 and their method of transcription. Provirus 22q11.21 (LTR Hs, FPKM = 26.11) is located 2.1 kb downstream from the expressed gene PRODH (Proline Dehydrogenase (oxidase) 1, FPKM = 11.53) but in the opposite transcriptional orientation. The 5’ LTR of 22q11.21 appears to drive proviral transcription in Tera-1 cells. Provirus 22q11.23 (FPKM = 26.94) appears to be transcribed solely through the use of an LTR Hs (FPKM = 0.31) located 551 bp upstream from the provirus. This transcript coincides with an annotated lincRNA (large intergenic non-coding RNA) [59]. See supplemental Figures S3 and S4 for more detail. Cartoon is not drawn to scale.