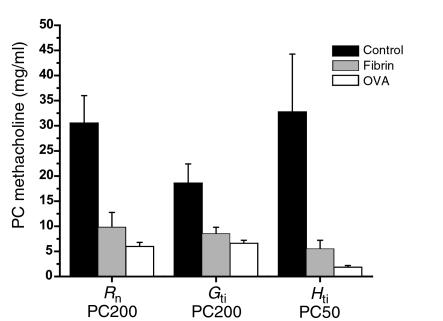
Figure 4.
Effect of fibrinogen followed by thrombin on airway hyperresponsiveness. Mice that received fibrinogen followed by thrombin (n = 7) had significantly increased airway hyperresponsiveness in terms of all parameters compared with mice that received saline alone (n = 7): Rn (saline alone, 30.5 ± 5.5, versus fibrinogen followed by thrombin, 9.8 ± 2.9; P < 0.01), Gti (saline alone, 18.5 ± 3.8, versus fibrinogen followed by thrombin, 8.5 ± 1.3; P < 0.01), and Hti (saline alone, 32.7 ± 12, versus fibrinogen followed by thrombin, 5.5 ± 1.7; P < 0.01). The degree of airway hyperresponsiveness seen in fibrinogen followed by thrombin mice was similar to that seen in mice with allergic airway inflammation (OVA) (n = 10): Rn (fibrinogen followed by thrombin, 9.8 ± 2.9, versus OVA, 5.95 ± 0.82), Gti (fibrinogen followed by thrombin, 8.5 ± 1.3, versus OVA, 6.57 ± 0.64), Hti (fibrinogen followed by thrombin, 5.5 ± 1.7, versus OVA, 1.83 ± 0.37).