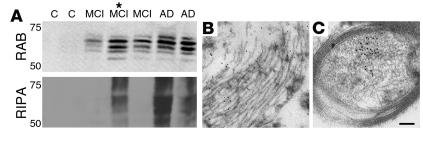
Figure 4.
ΔTau becomes increasingly insoluble with disease progression and is associated with tangle-like pathology at the ultrastructural level. Control (C), MCI, and AD temporal cortex samples were subjected to sequential fractionation into high-salt RAB and detergent-soluble RIPA fractions as previously described (50, 78) (A). ΔTau was detected in the soluble RAB fraction of MCI and AD but not control cases, suggesting that ΔTau production coincides with the early stages of cognitive decline in AD. In detergent-soluble RIPA fractions, ΔTau was only detected in higher-pathology MCI and AD cases, which suggests that ΔTau becomes more insoluble as AD progresses. *This patient was considered transitional between MCI and AD (see Methods). Immunogold electron microscopy demonstrated ΔTau at the ultrastructural level in association with early tangle-like pathology within a neuronal cell body (B) and a myelinated axon (C). Scale bar: 0.4 μm (B), 0.3 μm (C).