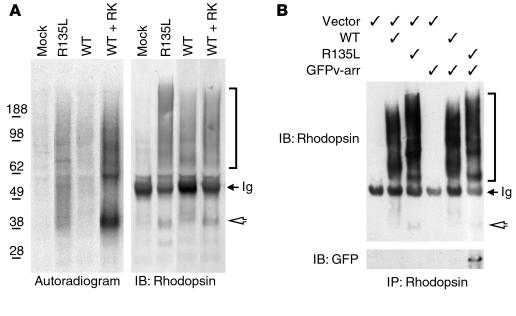
Figure 2.
Phosphorylation and v-arr association of R135L rhodopsin in HEK cells. (A) Immunoprecipitated rhodopsin, obtained from transfected cells that had been metabolically labeled with [32P] orthophosphate, were subjected to SDS-PAGE and either autoradiographed (left) or immunoblotted (right). (B) Rhodopsin immunoprecipitates obtained from cells transfected with pRK5 vector, rhodopsin and/or GFPv-arr (as indicated) were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with either anti-rhodopsin Ab (top) or anti-GFP Ab (bottom) (GFPv-arr: ∼75 kDa). Rhodopsin expressed in tissue culture is heterogeneously glycosylated and prone to forming higher-order aggregates (2, 5), which accounts for the broadened bands on SDS-PAGE. Arrowheads point to the rhodopsin monomer (∼40 kDa), and the brackets indicate the heterogeneous species of oligomerized rhodopsins. The electrophoretic patterns of R135L rhodopsins were distinct from those of WT rhodopsins, perhaps because of the conformation changes caused by the mutation. Some 50-kDa Ig heavy chains were reactive with the secondary antibodies (arrows). Results are representative of three experiments. IB, immunoblot; IP, immunoprecipitate.