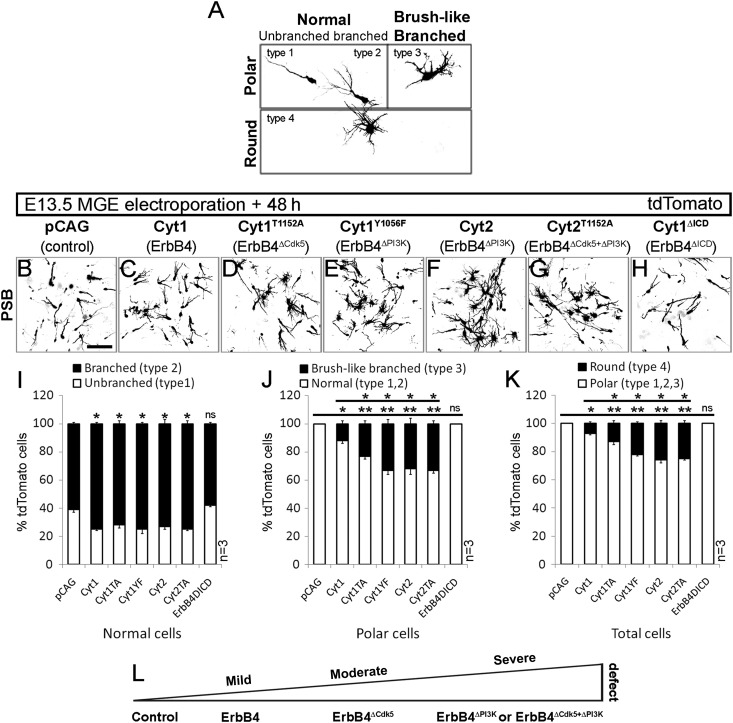
Figure 6.
Leading process morphology defects of cortical interneurons after loss of Cdk5 and PI3-kinase ErbB4 signaling. (A–H) tdTomato fluorescence, converted to grayscale, revealing morphology of migrating interneurons, 48-h postelectroporation of E13.5 MGE with control (pCAG; B) and ErbB4 (C–H) constructs (see Fig. 5). (A) Four types of MGE cell-leading process morphologies, observed at the PSB. (I) Percentage of unbranched (type 1) and branched (type 2) cells relative to total number of normal (type 1, 2) cells. (J) Percentage of brush-like branched (type 3) and normal (type 1, 2) cells relative to total number of polar (type 1, 2, and 3) cells. (K) Percentage of round (type 4) and polar (type 1, 2, and 3) cells relative to total cell number (type 1, 2, 3, and 4). (L) Schematic, indicating the severity of morphology defect in MGE cells in respect to altered ErbB4 signaling pathway. *P ≤ 0.05 (mild), **P ≤ 0.01 (moderate), ***P ≤ 0.005 (severe), t-test comparing against either control or Cyt1. Bar, 50 μm.