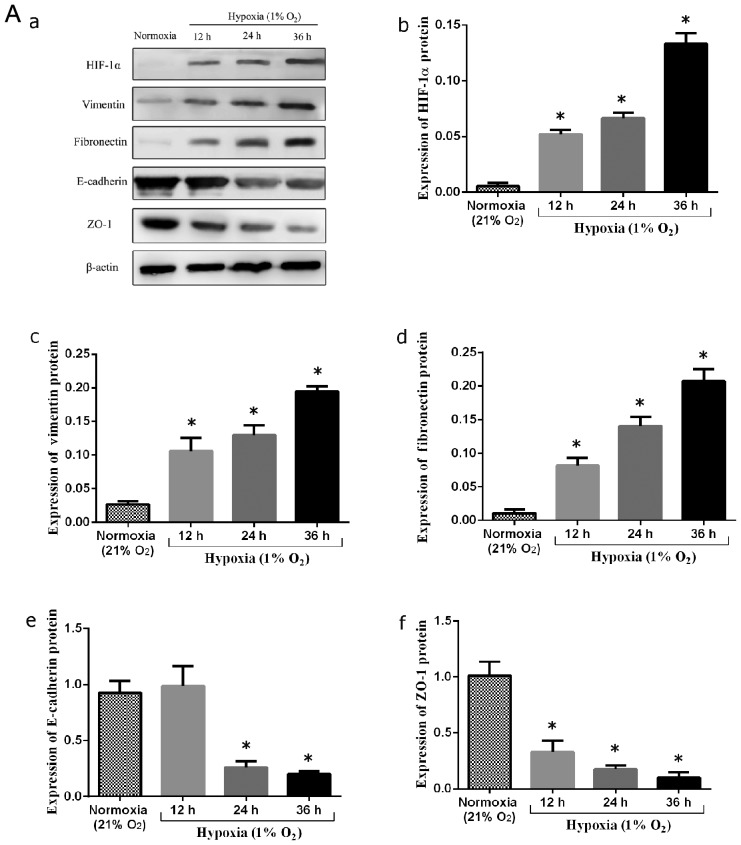
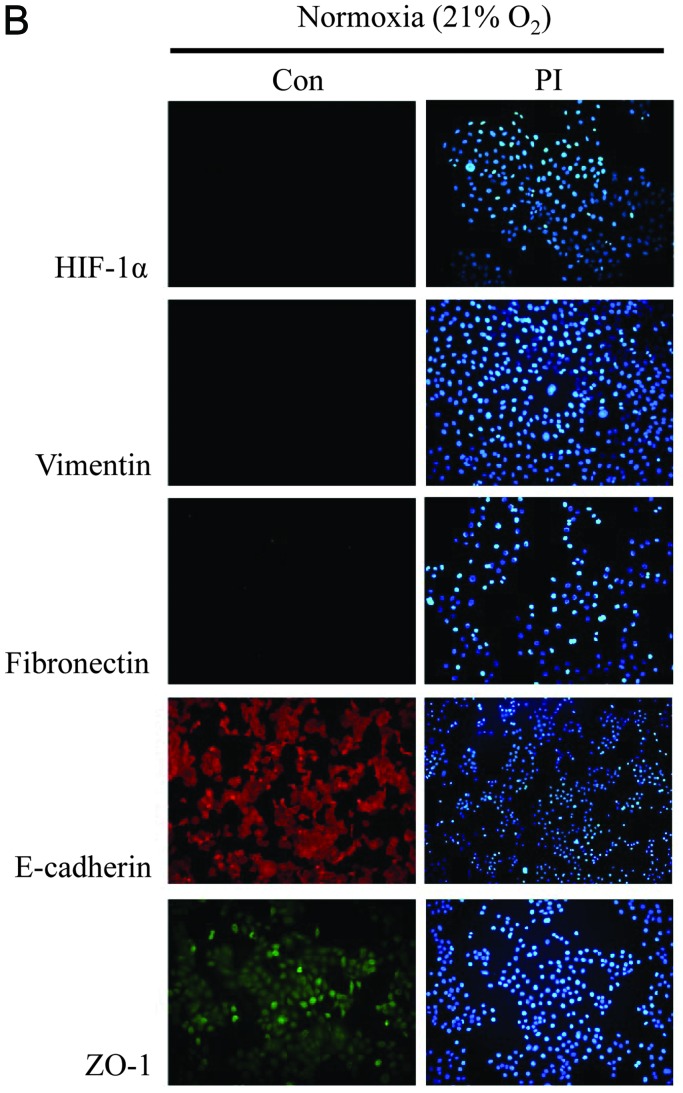
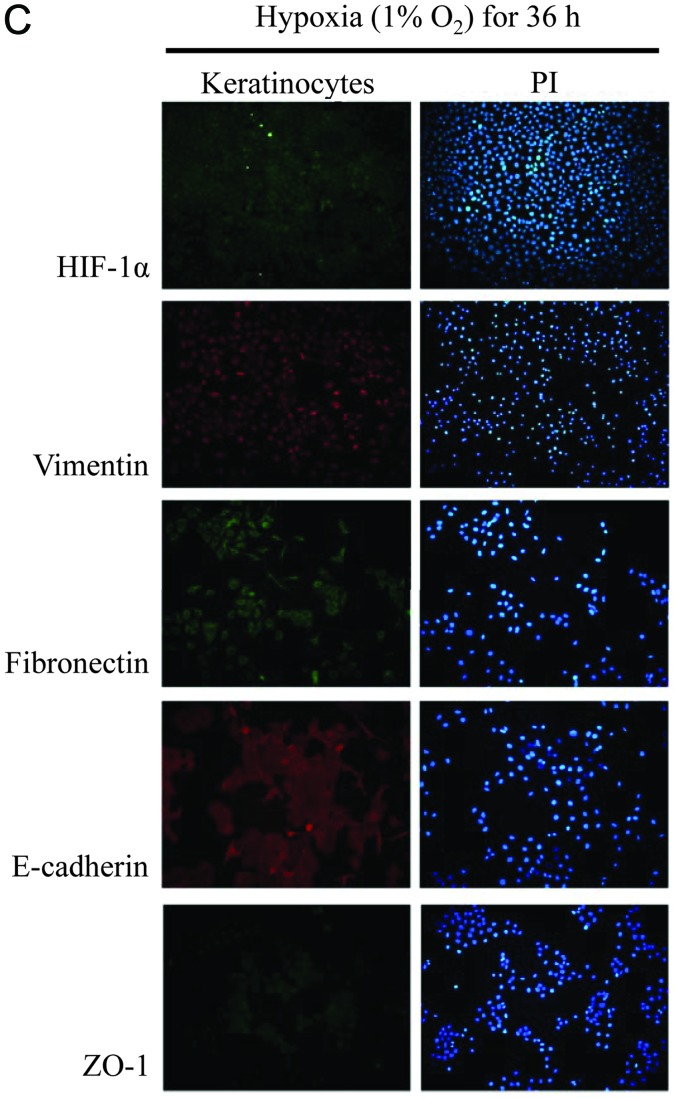
Figure 4.
(A) Analysis of alterations in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) marker and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) protein expression in keloid keratinocytes. (a) Keloid keratinocytes were cultured under normoxic (21% O2) and hypoxic conditions (1% O2) for different periods of time (12, 24 and 36 h). The expression of (b) HIF-1α, (c) vimentin, (d) fibronectin, (e) E-cadherin, and (f) zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) in keloid keratinocytes is indicated. *P<0.05 vs. keratinocytes under normoxic conditions (21% O2). Bars represent the means ± SD of 3 independent experiments. (B) Phenotype detection of keloid keratinocytes under normoxic conditions (21% O2) by immunofluorescence staining. The expression of HIF-1α and EMT-related markers was not detected in the nucleus or cytoplasm of the keloid keratinocytes after 36 h of culture under normoxic conditions. HIF-1α, vimentin and fibronectin expression was not detected. On the contrary, E-cadherin and ZO-1 were normally expressed and detected under an inverted fluorescence microscope. (C) EMT phenotype detection of keloid keratinocytes under hypoxic conditions (1% O2) by immunofluorescence staining. The protein expression of HIF-1α, vimentin and fibronectin was accumulated in the nucleus and cytoplasm of keloid keratinocytes after 36 h of culture under hypoxic conditions. E-cadherin and ZO-1 expression was reduced compared to the cells cultured under normoxic conditions, as observed under an inverted fluorescence microscope.