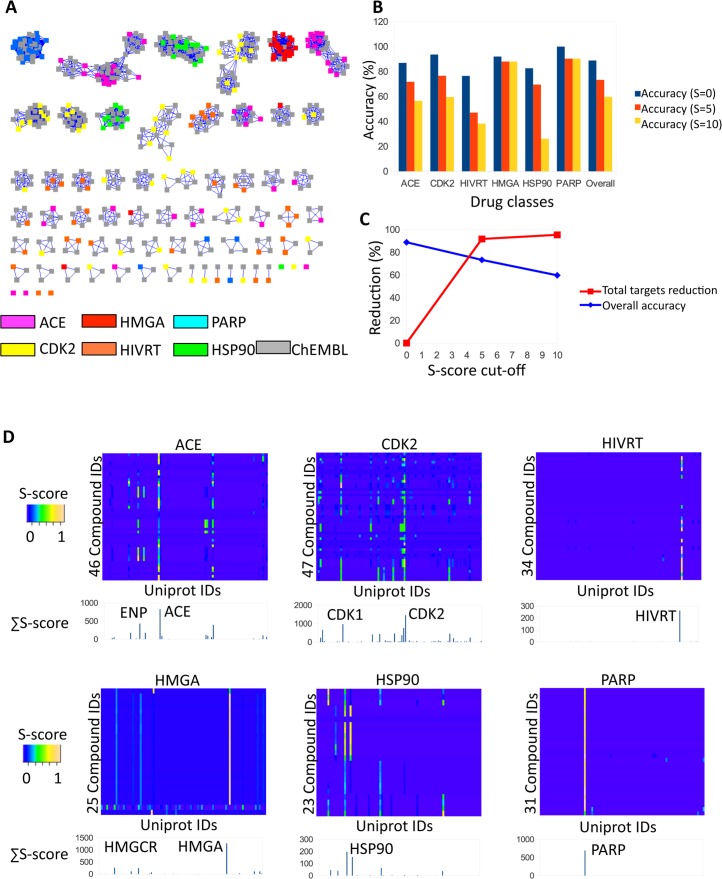
Fig 2. CSNAP validation using benchmark compounds.
(A) 206 compounds from six major drug classes (ACE, CDK2, HIVRT, HMGA, HSP90 and PARP) were analyzed using CSNAP with a Z-score cutoff of 2.5 and a Tanimoto coefficient (Tc) cutoff of 1. With the exception of 7 molecules, all compounds were ordered into chemical similarity subnetworks specific to each drug target. (B) Outcome of applying the neighbor counting function, S-score to predict the top 5 most common targets shared by the annotated-neighbor nodes of all input ligands within the CSN. The prediction accuracy (percentage of correctly predicted ligands) was determined by comparing the predicted target to ligand target annotations. CSNAP target prediction assessment for each drug class ranked by different S-score cutoffs (S-cutoff = 0, 5 and 10) gave an overall prediction accuracy of 89%, 73% and 60% respectively. (C) Comparison of the total percentage of target pool reduction (percentage of the total number of predicted targets with S-score cutoff over total number of predicted targets with S-score cutoff) against the overall prediction accuracy indicated that an S-score cutoff of 4 is optimal for hit enrichment and target virtual screening. (D) CSNAP target and off-target prediction for benchmark compounds. Predicted targets for the validation compounds were plotted against each drug class to identify targets and off-targets using Ligand-Target Interaction Fingerprints (LTIFs) analyzed on heat maps. The color intensity was scaled according to the S-score (0–1). Note that ACE and CDK2 inhibitors have predicted off-targets based on the additional coloring patterns, indicating drug poly-pharmacology. See S1 Fig for LTIF analysis of the combined drug classes.