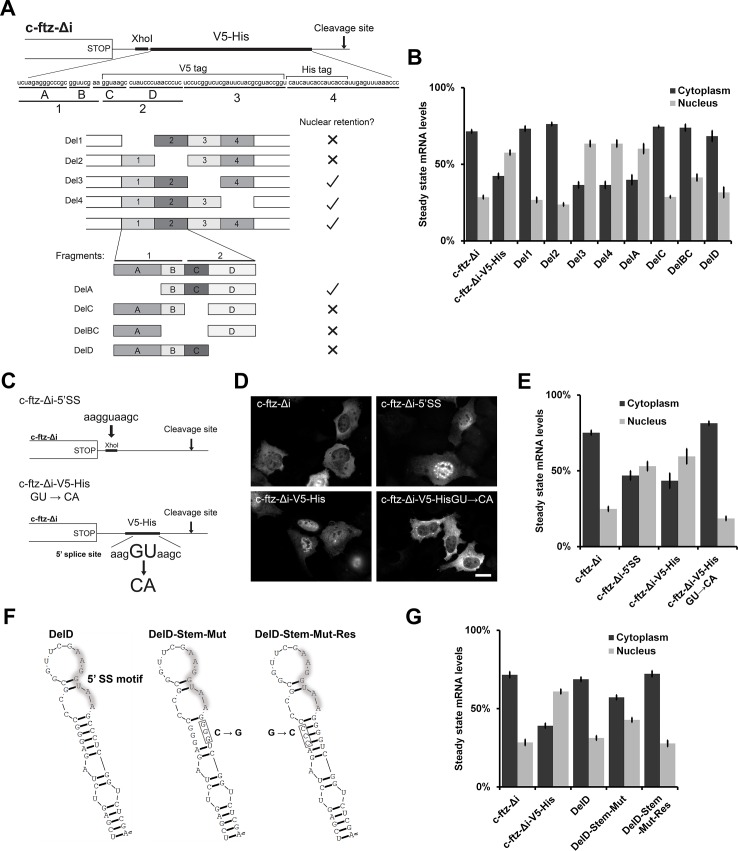
Fig 2. Mapping the minimal sequence in the V5-His element that disrupts cytoplasmic mRNA accumulation.
(A) Schematic of deletion mutants used to map the element responsible for the nuclear retention activity in the V5-His element. (B) U2OS cells were transfected with versions of c-ftz-Δi-V5-His gene lacking the various regions indicated in (A), and mRNA distribution was determined as in Fig 1C. Each bar is the average and standard error of at least three independent experiments, each experiment consisting of the average of at least 60 cells. (C) Schematic of constructs designed to test whether the 5’SS motif is responsible for nuclear retention. A consensus 5’SS motif was inserted into the 3’UTR of c-ftz-Δi to generate c-ftz-Δi-5’SS (top). The central GU nucleotide in the 5’SS motif was mutated to CA in c-ftz-Δi-V5-His to generate c-ftz-Δi-v5-His-GU→CA (bottom). (D-E) U2OS cells were transfected with the indicated versions of ftz and mRNA distribution was determined as in Fig 1C. Examples of ftz FISH images are shown in (D) and quantification of their distributions is shown in (E). Scale bar = 20μm. Each bar in E is the average and standard error of at least three independent experiments, each experiment consisting of the average of at least 60 cells. (F) Predicted secondary structure of the region surrounding the 5’SS motif (highlighted) in the c-ftz-Δi-V5-His-DelD construct and in the two stem-loop mutants. The RNA structures were generated using RNAStructure 5.03 [57]. (G) U2OS cells were transfected with the indicated versions of c-ftz-Δi-v5-His DelD and mRNA distribution was determined as in Fig 1C. Each bar is the average and standard error of at least three independent experiments, each experiment consisting of the average of at least 60 cells.