Fig. 9.
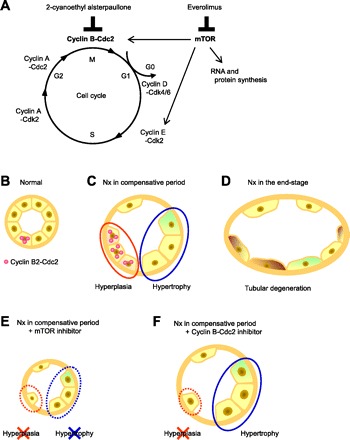
The hypothesized scheme of molecular responses in tubular epithelial hyperplasia and hypertrophy in chronic renal failure (CRF). A: molecular targets of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor and Cdc2 inhibitor in the cell cycle and mTOR pathway. B–F: renal proximal tubules of normal rats (B) and Nx rats (C–F). A portion of the renal epithelial cells in the proximal tubules was positive for Cyclin B2-Cdc2 (B). Hyperplasia via induction of Cyclin B2-Cdc2, G2-M cyclins, and hypertrophy simultaneously occurred in the compensative period in CRF rats (C). In end-stage CRF, tubular atrophy and degeneration were observed (D). E: proximal tubules treated with the mTOR inhibitor. Neither hyperplasia nor hypertrophy of tubular epithelial cells occurred, resulting in severe renal damage. F: proximal tubules treated with the Cyclin B-Cdc2 inhibitor. Only hyperplasia was inhibited, and a moderate reduction in renal function was observed.
