Figure 1.
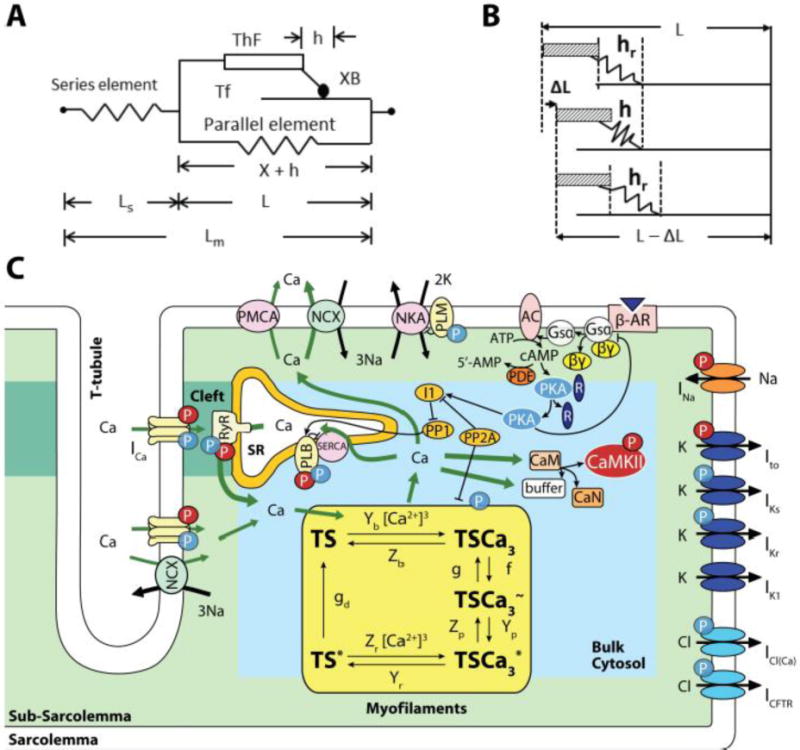
Model. A: Constitutive muscle unit, consisting of half-sarcomere length (L) composed of thick (ThF) and thin (Tf) filaments in parallel with an elastic element. The equivalent cross-bride (XB) representing all attached cross-bridges is part of the ThF. It attaches to the Tf by the mobile end of its elastic structure, with h elongation, defining an inextensible half-sarcomere length X = L − h. A series elastic element with length Ls accounts for compliant muscle ends and together with L make up total muscle length (Lm). B: Cross-bridge dynamics showing steadystate XB elongation (hr), its decrease due to ΔL and later return to hr at shorter half-sarcomere length (L-ΔL). C: Four compartment myocyte model: Bulk Cytosol, Cleft, sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) and subsarcolemmal space (Sub-SL) [25, 29] with ion currents as described by these authors. This model is coupled to the myofilament force development model consisting of 5-state troponin systems (TS) with Ca2+ binding. Each TS is composed of three adjacent troponin–tropomyosin regulatory units able to act cooperatively to bind Ca2+ in three successive steps. Troponin systems are: free TS; Ca2+ bound to TS without attached XBs (TSCa3), Ca2+ bound to TS with attached XBs in the weak state (TSCa3~), Ca2+ bound to TS with attached XBs in the power state (TSCa3*), and TS without Ca2+ with attached XBs in the power state (TS*). Baseline mechanical parameters and all changes used for ISO are in Table 1.
