Figure 6.
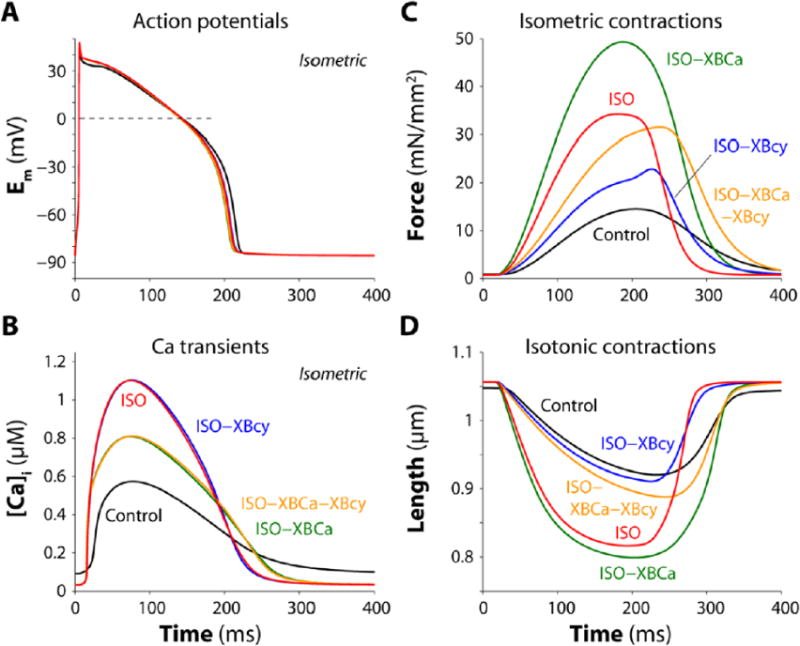
Simulation of AP, [Ca2+]i and isometric or isotonic twitches. Results are shown for control, ISO (100 nM), and ISO with suppression of different target effects (ISO-XBCa, ISO-XBcy and ISO-XBCa-XBcy). A: ISO slightly reduces APD, a response seen in all β-AS conditions. B: ISO and ISO-XBcy increase peak [Ca2+]i, its velocity of rise and faster decline (TCa50 and TCa90), while abrogation of conditions involving XBCa decrease the peak [Ca2+]i. C–D: ISO increases isometric force and isotonic shortening which is further enhanced upon eliminating ISO effect from XBCa (ISO-XBCa). Abrogation of ISO effect on XBcy (ISO-XBcy) blunts inotropy for force and shortening, while removing ISO effect on both contractile targets (ISO-XBCa-XBcy) allows the inotropic increase in force but not shortening (see also Table 4).
