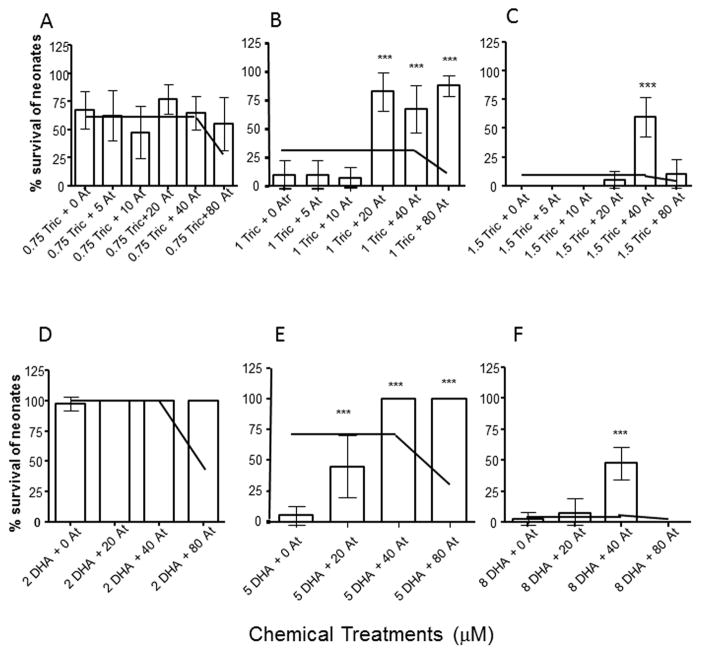
Fig. 3. The HR96 activator, atrazine induces a concentration-dependent interaction that protects daphnids from toxicity induced by triclosan or DHA.
Acute toxicity tests were performed with low (A), medium (B) and high (C) concentrations of triclosan coupled with multiple concentrations of atrazine, or low (D), medium (E), and high (F) concentrations of DHA coupled with multiple concentrations of atrazine. Data are provided as mean ± 95% confidence intervals (n = 10 per treatment). Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.) Statistically significant data is in comparison to the control group. The independent joint action model from CATAM was used to predict daphnid survival under mixture conditions with the average 95% confidence intervals from the toxicity tests used to predict variance in the model. The independent joint action model prediction is shown as a line in each graph.