Figure.
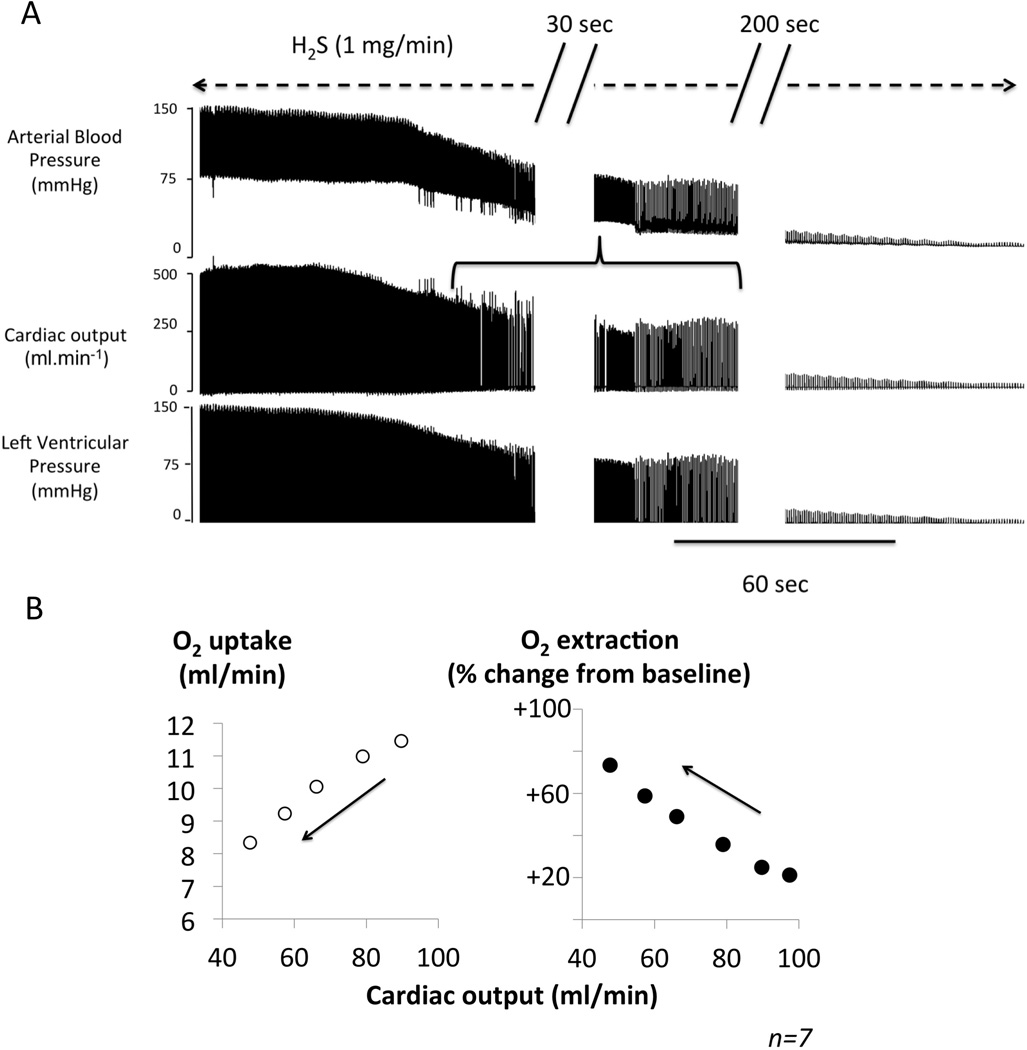
Panel A. Original recording of the changes in arterial blood pressure, cardiac output and the left ventricular pressure, during H2S infusion in a 500 g rat receiving a solution of sulfide made from NaHS (1 mg/min). There was a rapid decrease in cardiac output, arterial pressure and left ventricular pressure, which led to asystole, within 5 minutes. The horizontal bracket shows the period at which of cardiac output was determined for the computations shown in B. Panel B. V̇O2 (left panel) and the change in O2 extraction as % from baseline (Right panel) as a function of cardiac output. 10 second-averaged data obtained from 7 rats during the first minutes of an infusion of H2S at toxic levels (2 mg/min) are shown. Cardiac output dropped dramatically, while oxygen extraction increases reflecting a proportionally higher fall in O2 delivery than in O2 utilization. Note that PaO2 and thus the arterial O2 content was prevented to decrease by mechanical ventilation throughout the period of infusion.
