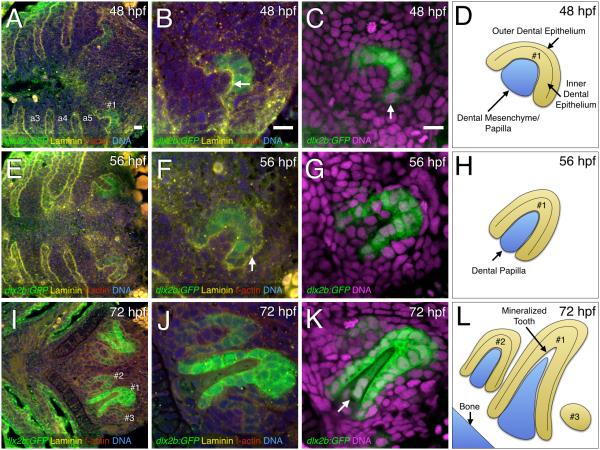
Figure 1. Fluorescence visualization of cellular details during tooth germ morphogenesis.
(A, E, I) Ventral views, anterior to the left, of the zebrafish pharyngeal region. (B-C, F-G, J-K) Closeups of right-side tooth germs. (A-B, E-F, I-J) Four-color stains of dlx2b:GFP reporter expression (green), laminin protein (yellow), f-actin (red), and DNA (blue). (C, G, K) Two-color stains with dlx2b:GFP (green) and DNA (magenta). (A-B) Laminin expression at 48 hpf and 56 hpf stages at the boundaries of the pharyngeal arches (a3-a5) as well as the interface between the dental epithelium and dental mesenchyme of tooth germ #1 (B, arrow). (C) dlx2b:GFP reporter expression mostly in the inner dental epithelium (arrow). (D) Schematic drawing of a early morphogenesis stage tooth germ #1 at 48 hpf. (E-F) Laminin expression highlighting the outer dental epithelium in a late morphogenesis stage tooth germ #1 at 56 hpf (F, arrow). (G-H) dlx2b:GFP expression in the inner dental epithelium and schematic drawing. (I-J) F-actin staining along with dlx2b:GFP expression in cell differentiation stage tooth germ #1 at 72 hpf. Tooth germs #2 and #3 are also present. (K) dlx2b:GFP expression in the inner dental epithelium and the dental papilla (arrow) at 72 hpf. Tooth germs #2 and #3 are mostly outside the focal plane in this specimen. (L) Schematic drawing of typical orientations of the tooth germs at 72 hpf. Scale bars = 10 μm (A-C).