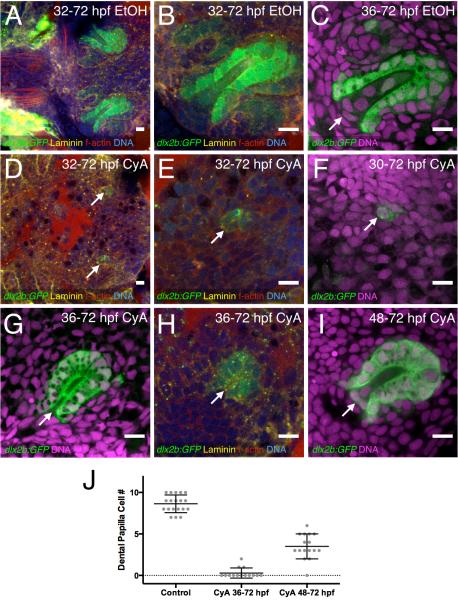
Figure 3. Hedgehog signaling is required for dental papilla formation.
(A-C) dlx2b:GFP expression in normal-appearing tooth germs exposed to 0.2% EtOH as a control from 32 or 36-72 hpf. The base of the dental papilla of tooth #1 is indicated (C, arrow). (D-F) Tooth forming region after 50μM CyA exposure from 30 or 32-72 hpf, showing a few disorganized-appearing GFP-positive cells (arrows). (G-H) Tooth germ after later CyA treatment from 36-72 hpf lacking a dental papilla (arrow). (I) Tooth germ after CyA exposure from 48-72 hpf, with a smaller than normal dental papilla (arrow). (J) Graph of dental papilla cell numbers at 72 hpf. Gray dots represent individual counts, central bars are the mean, and flanking error bars indicate standard error. All three pairwise comparisons are significantly different. Tooth germ orientations are as in Fig. 1. Scale bars = 10 μm.