Figure 1.
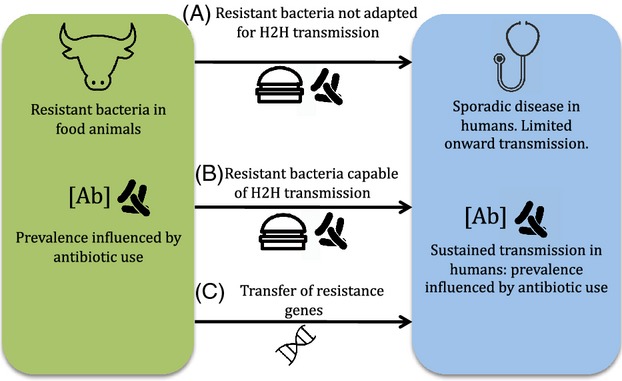
Schematic illustration of possible links between antibiotic use in agriculture and human disease. The prevalence of resistant bacteria in agriculture is influenced by antibiotic use in that setting. The impact of infection depends crucially on the capacity for sustained human to human (H2H) transmission. Arrows linking the two populations represent: a) direct transmission of bacteria not adapted to transmission in humans via the food chain (e.g Campylobacter, Salmonella) or direct contact with animals; b) direct transmission of organisms already adapted to transmission in humans; c) transfer of resistance genes from the agricultural setting into pathogens transmitting among humans.
