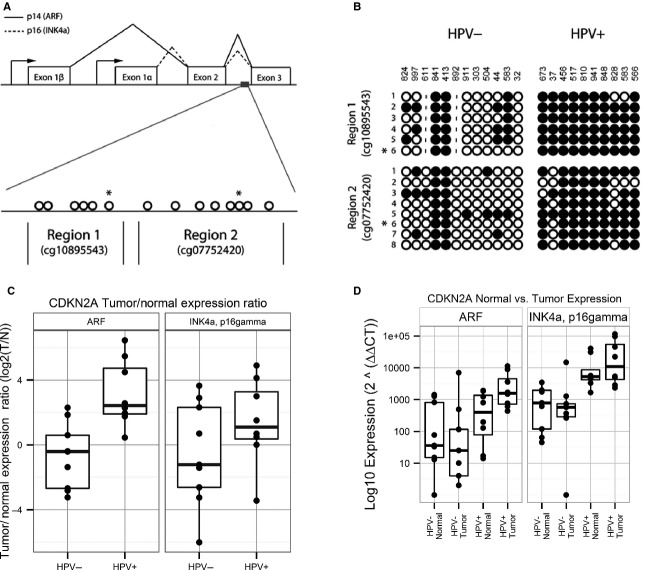
Figure 3.
(A) Genomic organization of the chromosome 9p21 CDKN2A locus encoding p16INK4A and p14ARF. Proteins p16(INK4A) and p14(ARF) share exons 2 and 3 but have a distinct exon 1. RNA transcripts are translated in different reading frames to generate two separate protein products. Alternate promoter sites are indicated by arrows. Location of the CpG island corresponding to the downstream region (9:21958106-21958899) is indicated by a grey box. Also shown are two DNA segments located within the CDKN2A downstream region that was tested for DNA methylation by bisulfite sequencing. Individual CpG loci to be tested within each region are indicated by open circles; those indicated with an asterisk correspond to the location of Illumina beadchip loci cg10895543 and cg07752420. (B) Measurement of CpG methylation observed in the CDKN2A downstream region of HPV+ and HPV− primary OPSCC tumors by bisulfite sequencing. Patient identifiers are indicated on the top; individual CpG loci for each region are shown at the left. Methylated CpG loci are indicated by closed circles; unmethylated CpG loci are indicated by open circles. Positions of CpG loci included on the Illumina HumanMethylation27 BeadChip are indicated by an asterisk. (C) Real-time PCR measurements of gene expression for p14(ARF), p16(INK4A), and p16 gamma in oropharyngeal tumor and adjacent normal tissues from HPV-positive and HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancer cases. The panel shows expression changes (tumor/normal ratio) in 8 HPV+ and HPV− tumor samples following log2 transformation. Statistical significance of gene expression differences between HPV-positive and HPV-negative cases were assessed by Wilcoxon Rank Sum. (D) Analysis of p14(ARF), p16(INK4A), and p16 gamma expression looking individually at normal adjacent mucosa and primary OPSCC tumors as independent populations in HPV-positive and HPV-negative patients.