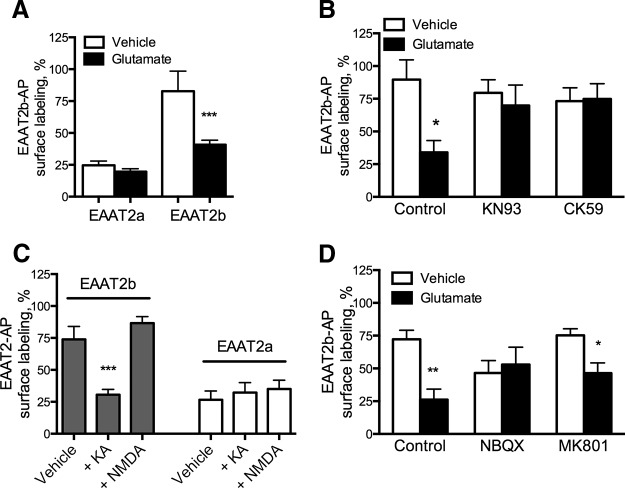
Figure 6.
EAAT2b is internalized in response to AMPA/KA receptor-mediated CaMKII activation. A, Astrocytes were transiently transfected with EAAT2a-AP or EAAT2b-AP and cell surface expression was assessed after 30 min of treatment with vehicle or glutamate (250 μm). This treatment had no significant effect on EAAT2a, but the surface localization of EAAT2b was significantly decreased by glutamate. ***p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA (n = 14, 28, 20, 28). B, Inhibition of CaMKII with CK59 (100 μm) or KN93 (10 μm) also prevented EAAT2b-AP internalization in primary astrocytes. *p < 0.05 by two-way ANOVA (n = 9, 8, 10, 7, 10, 10). C, EAAT2b-AP cell-surface expression in primary astrocytes also decreases in response to kainate, but not NMDA (100 μm each), indicating an AMPA/KA receptor mediates EAAT2b internalization. EAAT2a-AP expression was unaltered by treatment with the glutamate receptor agonists. ***p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA (n = 17, 20, 4, 12, 6, 4). D, The AMPA/KA receptor antagonist NBQX (100 μm) blocked the effects of glutamate on the surface expression of EAAT2b-AP-transfected astrocytes. The NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 (10 μm) had no significant effect. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 by two-way ANOVA (n = 9, 6, 8, 6, 9, 9). Error bars indicate SEM.