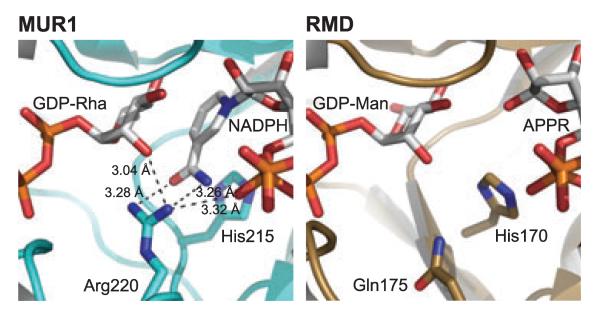
Fig. 11.
The potential hydrogen-bonding interactions of a conserved GMD arginine. The active sites of A. thermoaerophilus RMD and Ar. thaliana MUR1 are shown in equivalent orientations for comparison. MUR1 Arg220 is conserved in all GMDs, and during catalysis may coordinate with a cofactor phosphate, the substrate hexose, and the nicotinamide carboxyamide. The distances between these groups in the MUR1 crystal structure are indicated. In the RMD structure, the position of the MUR1 Arg220 is occupied by a glutamine, and this amino acid side chain is too short to mediate the same protein–ligand interactions. This may account for the disordering of the nicotinamide ring in the RMD crystal.